Red Eye
Key Takeaway: Most red eye cases resolve naturally within 24-48 hours, but persistent redness lasting more than a week—especially when accompanied by pain, vision changes, or discharge—requires immediate professional evaluation to prevent potential complications.
Red, bloodshot eyes are among the most common reasons patients visit eye care professionals. Whether you’ve awakened to find your reflection staring back with inflamed, irritated eyes or noticed gradual redness developing throughout your workday, understanding when to treat symptoms at home versus seeking professional care can make the critical difference between swift recovery and serious complications.
For Seattle’s workforce, particularly those in technology and other screen-intensive industries, red eye concerns have become increasingly prevalent. The combination of extended digital device usage, environmental factors unique to the Pacific Northwest, and the demands of professional life creates a perfect storm for eye irritation and strain.
Understanding Red Eye: What Causes Bloodshot Eyes?
Red eye occurs when tiny blood vessels beneath your eye’s surface—specifically in the conjunctiva and sclera—become enlarged, inflamed, or dilated. This vascular response transforms the normally white appearance of your eye into varying shades of pink or red, creating the characteristic “bloodshot” appearance that signals underlying irritation or injury.
The severity of redness doesn’t always correlate with the seriousness of the condition. Some dramatic-looking red eyes result from minor irritants, while certain serious conditions may present with only subtle redness accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
The condition can affect one or both eyes simultaneously and may develop gradually over days or appear suddenly within minutes of exposure to an irritant or injury. Understanding this variability helps patients make informed decisions about the urgency of their situation.
Most Common Red Eye Causes: From Digital Strain to Serious Conditions
The modern lifestyle presents numerous opportunities for eye irritation, ranging from environmental factors to underlying medical conditions that require professional attention.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Digital Eye Strain and Computer Vision Syndrome
Seattle’s technology-driven economy means countless professionals spend eight or more hours daily focused on computer screens, tablets, and smartphones. This prolonged near-work creates a cascade of physiological changes that frequently manifest as red, irritated eyes.
When we focus on screens, our natural blink rate decreases by approximately 60%, reducing the eye’s natural lubrication system. Additionally, the sustained accommodation required for near-focus work places strain on the ciliary muscles, contributing to overall eye fatigue and surface irritation.
When your eyes cannot produce adequate tears or when tears evaporate too quickly, chronic dry eye develops. Recent epidemiological studies indicate that approximately 10-20% of the population over 40 years of age experience moderate to severe dry eye symptoms, with diagnosed dry eye disease affecting an estimated 5-7% of US adults overall.
The condition disproportionately affects women (approximately 8%) compared to men (approximately 3%) and increases significantly with age. Environmental factors common to the Seattle area—including seasonal humidity changes, indoor heating systems, and air conditioning—can exacerbate symptoms.
The Pacific Northwest’s diverse plant life creates year-round allergen challenges. When airborne particles such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores contact the eye’s surface, susceptible individuals experience histamine release, causing blood vessels to expand and become inflamed.
Contact Lens Complications
Extended wear, inadequate cleaning protocols, or sleeping in contacts not designed for overnight use can lead to corneal irritation, reduced oxygen flow, and subsequent redness. Contact lens-related red eye often indicates the need for fitting adjustments or hygiene education.
Medical Conditions Causing Red Eye
Conjunctivitis represents inflammation of the thin membrane covering the eye’s white portion and inner eyelid surfaces. This condition can result from viral infections (most common), bacterial infections, or allergic reactions, each requiring different treatment approaches.
Viral conjunctivitis typically begins in one eye and may spread to the other, often accompanying upper respiratory infections. Bacterial conjunctivitis frequently produces thicker discharge and may respond to antibiotic treatment. Allergic conjunctivitis usually affects both eyes simultaneously and correlates with other allergy symptoms.
This common condition involves inflammation of the eyelid margins, often resulting from bacterial overgrowth or dysfunction of the oil glands along the eyelid edges. Blepharitis creates a cycle of irritation that frequently leads to red, uncomfortable eyes and may require ongoing management.
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
When small blood vessels rupture beneath the conjunctiva, blood spreads across the eye’s surface, creating a dramatic red appearance that often alarms patients. Despite its striking appearance, subconjunctival hemorrhage is typically benign and resolves without treatment within 1-2 weeks.
Common triggers include sudden pressure increases from coughing, sneezing, heavy lifting, or straining. Patients taking blood-thinning medications may experience these hemorrhages more frequently.
Red Eye Symptoms: Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Red eye presentations vary significantly based on underlying causes, making symptom assessment crucial for determining appropriate care urgency.
Mild Symptoms (Often Self-Manageable)
- Light scratching or foreign body sensation
- Minimal tearing or watery discharge
- Slight sensitivity to bright lighting
- Redness without pain or vision changes
- Symptoms that improve with rest or basic care measures
Concerning Symptoms (Require Professional Evaluation)
- Eye pain beyond mild discomfort
- Vision changes, including blurring, halos, or reduced acuity
- Photophobia (severe light sensitivity)
- Discharge that is thick, yellow, or green in color
- Symptoms persisting beyond one week or worsening over time
- Systemic symptoms, including fever, headache, or nausea
The presence of pain and vision changes together represents a particularly concerning combination that warrants immediate professional attention, as these symptoms may indicate conditions requiring urgent intervention.
When to See a Seattle Optometrist for Red Eye: Emergency vs. Urgent Care
Understanding the difference between conditions requiring emergency care, urgent professional attention, or home management can prevent both unnecessary anxiety and dangerous delays in treatment.
Red Eye Emergency Warning Signs
Seek immediate emergency care or call 911 if you experience:
- Red eye following penetrating injury or trauma
- Sudden severe headache with vision changes and confusion
- Halos or rainbows around lights, especially with nausea
- Complete or partial vision loss in the affected eye
- Fixed, non-reactive pupil with severe pain
Urgent Professional Care Needed
Contact an eye care provider within 24 hours for:
- Eye pain that interferes with daily activities
- Vision changes that don’t resolve with blinking
- Thick, purulent discharge with crusting
- Red eye persisting longer than 48-72 hours
- Light sensitivity that prevents normal activities
- Foreign body sensation that doesn’t resolve with irrigation
Why Professional Evaluation Matters
A comprehensive eye examination requires specialized equipment, particularly the slit lamp, which provides magnified, illuminated views of eye structures impossible to achieve through standard examination methods. Many conditions causing red eye—including some requiring immediate treatment—can only be accurately diagnosed through professional evaluation.
Moreover, certain treatments, particularly topical steroids, should never be prescribed without proper examination, as their inappropriate use in specific conditions can worsen outcomes dramatically.
Effective Red Eye Treatment: Home Remedies vs. Professional Care
Treatment approaches range from simple home remedies appropriate for minor irritation to sophisticated medical interventions for serious conditions.
Safe Home Remedies for Red Eyes
Immediate Relief Measures
- Cool compresses: Apply clean, damp washcloths to closed eyes for 10-15 minutes several times daily
- Gentle eyelid hygiene: Use warm water and mild soap to clean eyelid margins, particularly beneficial for blepharitis-related redness
- Artificial tears: Preservative-free lubricating drops can provide relief for dry eye-related redness
- Environmental modifications: Increase humidity, reduce air circulation directed at the face, and take regular breaks from screen work
Artificial Tears Selection
Not all eye drops are equivalent. Artificial tears work by either supplementing the aqueous (water) component or the lipid (oil) component of natural tears. For frequent use—more than four times daily—preservative-free formulations prevent additional irritation from chemical preservatives.
For contact lens wearers, ensure drops are specifically labeled as compatible with contact lens wear, as some formulations can interact negatively with lens materials.
Professional Treatment Options
Prescription Medications
Based on the underlying cause, eye care professionals may prescribe:
- Antibiotic drops or ointments for bacterial infections
- Antiviral medications for herpes-related conditions
- Topical steroids for inflammatory conditions (when appropriate)
- Immunosuppressive agents like cyclosporine for chronic dry eye
- Allergy medications, including antihistamine drops for allergic conjunctivitis
Advanced Treatments
For chronic conditions, particularly severe dry eye, advanced interventions may include:
- Punctal plugs to conserve natural tears
- Autologous serum tears created from the patient’s own blood
- Prescription tear stimulants to increase natural production
- In-office procedures, such as intense pulsed light therapy for meibomian gland dysfunction
What NOT to Do with Red Eyes: Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding potentially harmful self-treatment approaches protects against inadvertently worsening conditions.
Critical Mistakes to Avoid
Never rub irritated eyes, as this introduces bacteria from hands while potentially causing corneal abrasions or spreading infections from one eye to the other.
Avoid long-term use of redness-reducing drops (such as those containing tetrahydrozoline or naphazoline) beyond three days, as rebound redness often occurs when discontinued, potentially creating dependency.
Don’t continue wearing contact lenses with red eye symptoms, as this can trap irritants against the cornea and prevent proper healing.
Avoid homemade remedies, including tea bags, breast milk, or honey applications, as these introduce contamination risks without proven benefits and may delay appropriate treatment.
Never share eye medications or use expired drops, as contamination and reduced efficacy can worsen conditions.
Recent Research and Advances in Red Eye Treatment
Current research continues to expand our understanding of eye surface health and optimal treatment approaches.
Breakthrough Studies in Eye Health
Recent research has demonstrated promising developments in eye care treatment. Red light therapy (RLT) has shown remarkable, multifaceted effects in ophthalmology, including slowing myopia progression, protecting retinal cells in glaucoma, reducing inflammation in age-related macular degeneration, and relieving symptoms of dry eye disease.
A pioneering UCL study published in Scientific Reports found that just three minutes of exposure to deep red light once a week, when delivered in the morning, can significantly improve declining eyesight. While this research is still emerging, it represents the innovative approaches being developed to address eye health concerns.
Understanding Red Eye Prevalence
Research involving 840 patients found that the most common cause of red eye was conjunctivitis at 30%, followed by foreign bodies at 23.2%, and trauma at 8.6%. The most common eye symptoms with eye redness were eye irritation (57%), tears in the eyes (49%), and swollen eyelid (30%).
These findings help practitioners prioritize differential diagnoses and guide patients toward appropriate care pathways based on symptom presentations.
Red Eye Prevention for Seattle Professionals: Digital Eye Strain Solutions
Prevention strategies must account for the realities of modern professional life while addressing environmental factors specific to the Pacific Northwest.
Workplace Eye Health for Seattle Professionals
Digital Device Management
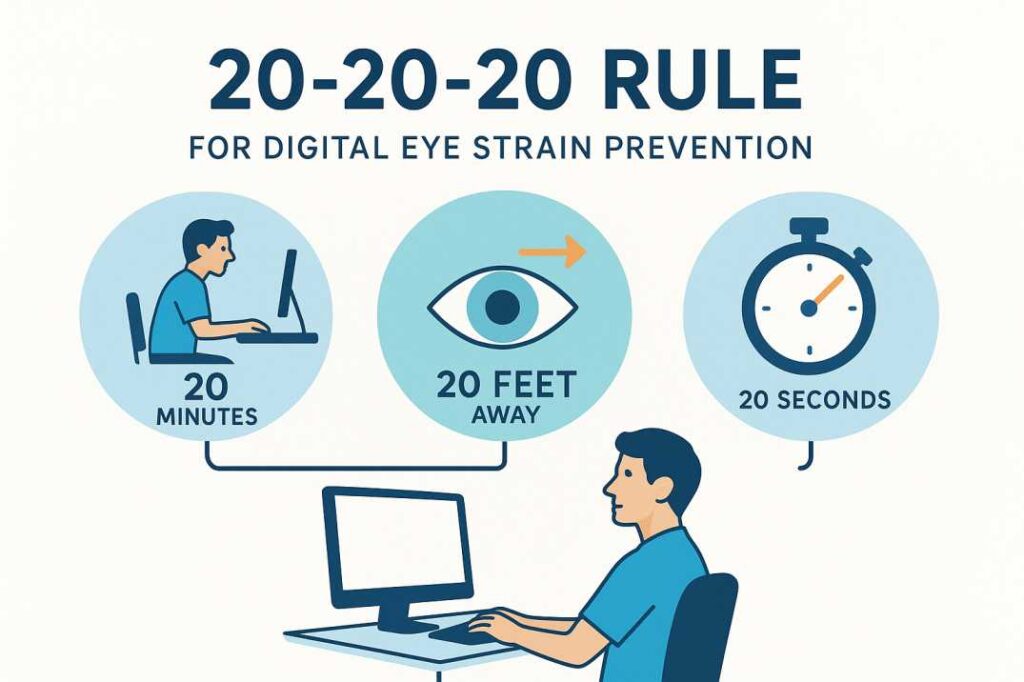
Current research shows that taking regular breaks from screen work is beneficial for reducing digital eye strain, though the specific 20-20-20 timing may be less critical than the principle of frequent visual breaks. Studies indicate that any break from repetitive computer work helps reduce eye strain symptoms.
Environmental Controls
- Position screens 20-26 inches from the eyes with the top at or slightly below eye level.
- Use appropriate task lighting to minimize glare
- Maintain indoor humidity between 30-50% when possible
- Consider blue light filtering options, though evidence for their effectiveness remains mixed
Workstation Ergonomics
Proper workstation setup reduces the postural strain that often accompanies visual discomfort. Monitor positioning, keyboard height, and chair adjustment all contribute to overall comfort during extended computer use.
General Prevention Strategies
Hand Hygiene: Regular handwashing, particularly before any eye contact, prevents the introduction of bacteria and viruses that commonly cause infectious conjunctivitis.
Contact Lens Care: Strict adherence to replacement schedules, proper cleaning protocols, and appropriate wear times prevents most contact lens-related complications.
Allergen Management: For susceptible individuals, monitoring local pollen counts, using air filtration systems, and pre-treating with allergy medications during high-exposure periods can prevent allergic reactions.
Eye Protection: Safety glasses for appropriate activities, sunglasses for UV protection, and protective eyewear for sports prevent trauma-related red eye incidents.
Finding the Best Seattle Optometrist for Red Eye Treatment
Selecting appropriate eye care involves understanding the qualifications, services, and approach that best meet your individual needs.
What to Look for in an Optometrist
Comprehensive Diagnostic Equipment
Modern eye care requires sophisticated diagnostic tools. Look for practices equipped with:
- Slit lamp biomicroscopes for detailed anterior segment examination
- Digital retinal imaging for comprehensive posterior segment evaluation
- Tear film analysis equipment for dry eye assessment
- Corneal topography for contact lens fitting and corneal evaluation
Specialized Expertise
Seek providers with demonstrated experience in:
- Dry eye management, including advanced treatment modalities
- Contact lens specialization, particularly for difficult-to-fit cases
- Ocular surface disease treatment and ongoing management
- Emergency eye care availability and protocols
Practice Philosophy and Approach
Consider providers who emphasize:
- Comprehensive examinations that go beyond basic vision testing
- Patient education to help you understand conditions and treatments
- Coordinated care with other healthcare providers when appropriate
- Accessibility for urgent concerns and follow-up care
Questions to Ask Your Eye Care Provider
During consultations for red eye concerns, consider asking:
- What is the most likely cause of my symptoms?
- Are there lifestyle modifications that could prevent recurrence?
- What warning signs should prompt immediate contact?
- How will we monitor my condition over time?
- What are the potential complications if left untreated?
Special Considerations for Different Life Stages
Red eye causes and management considerations vary significantly across age groups, requiring tailored approaches for optimal outcomes.
Young Adults and Professionals (20s-40s)
This demographic commonly experiences red eye related to:
- Extended screen exposure from professional and personal device use
- Contact lens complications from busy lifestyles are affecting proper care
- Stress-related symptoms, including tension and sleep deprivation effects
- Environmental allergies are particularly prevalent during career establishment years, with changing locations
Management often focuses on lifestyle modifications, workplace ergonomics, and establishing sustainable eye care routines that accommodate professional demands.
Middle-Aged Adults (40s-60s)
Age-related changes begin affecting eye comfort and health:
- Presbyopia development creates additional focusing strain
- Hormonal changes, particularly in women, affect tear production
- Medication side effects from treatments for other health conditions
- Systemic disease onset, including diabetes and autoimmune conditions that affect eye health
This group benefits from comprehensive health assessment and coordination between eye care and primary care providers.
Older Adults (60+)
Seniors face increased risks requiring vigilant attention:
- Age-related dry eye from decreased tear production and quality
- Medication interactions from multiple prescriptions affecting eye health
- Systemic disease complications require ongoing monitoring
- Decreased healing capacity makes prevention increasingly important
Regular preventive care becomes crucial for maintaining eye health and preventing complications that could significantly impact quality of life.
Living with Chronic Red Eye Conditions
For individuals with ongoing conditions such as dry eye disease or recurrent allergic conjunctivitis, developing comprehensive management strategies improves both comfort and long-term outcomes.
Daily Management Strategies
Environmental Controls
- Use humidifiers to maintain optimal indoor moisture levels
- Install air filtration systems to reduce allergen exposure
- Position fans and air vents to avoid direct air flow across the face
- Consider wraparound sunglasses for outdoor protection against wind and UV exposure
Routine Care Protocols
- Establish consistent eyelid hygiene routines using warm compresses and gentle cleaning
- Use preservative-free artificial tears on a regular schedule rather than waiting for symptoms.
- Maintain adequate hydration and consider omega-3 fatty acid supplementation under professional guidance.
- Schedule regular follow-up appointments for condition monitoring and treatment adjustment.
Workplace Accommodations
Professional environments can often accommodate employees with chronic eye conditions:
- Adjustable monitor positioning and ergonomic workstation setup
- Task lighting modifications to reduce glare and optimize visual comfort
- Regular break policies for employees requiring frequent eye rest
- Air quality consideration, including desk fans and air purification systems
The Economic Impact of Untreated Red Eye Conditions
Beyond personal discomfort, untreated or inadequately managed red eye conditions create broader economic consequences affecting individuals, employers, and healthcare systems.
Individual Costs: Lost productivity, increased healthcare utilization, reduced quality of life, and potential complications requiring more expensive interventions.
Workplace Impact: Reduced employee productivity, increased absenteeism, higher healthcare benefit costs, and potential safety concerns in certain industries.
Healthcare System Effects: Emergency department visits for non-urgent conditions, delayed diagnosis of serious conditions, and increased complexity of care due to delayed treatment.
Early intervention and appropriate management prevent many of these downstream costs while improving outcomes for affected individuals.
Emergency Eye Care Resources in Seattle
Preparation for eye emergencies improves outcomes when urgent situations arise.
When Every Minute Counts
For true eye emergencies:
- Know your eye care provider’s emergency contact information and after-hours protocols
- Identify the nearest emergency room with ophthalmology consultation services
- Understand basic first aid for eye injuries, including appropriate irrigation techniques
- Keep emergency contact numbers readily available in multiple locations
Building Your Eye Care Team
Establish relationships with eye care professionals before problems arise. Regular comprehensive eye examinations create baseline documentation and familiarity that proves invaluable during urgent situations.
Consider building relationships with:
- Primary optometrist for routine care and initial problem assessment
- Ophthalmologist referral contacts for surgical consultations when needed
- Emergency eye care services are available in your area
Conclusion and Next Steps
Red eye, while frequently benign, requires thoughtful assessment to distinguish between conditions appropriate for home management and those requiring professional intervention. Understanding the spectrum of causes—from simple environmental irritation to sight-threatening emergencies—empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
For Seattle’s professional community, the intersection of digital device demands, environmental factors, and busy lifestyles creates unique challenges requiring proactive management strategies. Success depends on recognizing early warning signs, implementing appropriate preventive measures, and maintaining relationships with qualified eye care professionals.
Key Takeaways for Optimal Eye Health
- Monitor symptom patterns: Duration, severity, and associated symptoms guide care decisions.
- Prioritize prevention: Workplace ergonomics, proper contact lens care, and environmental controls prevent many red eye episodes.
- Seek timely evaluation: Professional assessment for persistent or concerning symptoms prevents complications.s
- Maintain ongoing relationships: Regular eye care establishes baselines and ensures prompt attention for urgent concerns.
- Stay informed: Understanding your personal risk factors and triggers enables better self-management
References and Medical Resources
This article is based on peer-reviewed research and authoritative medical sources. For additional information, consult these key resources:
1. Clinical Research on Red Eye Causes
Common causes of red eye presenting in northern Iran – PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5711369/
Comprehensive study of 840 patients identifying the most common causes of red eye, including conjunctivitis (30%), foreign bodies (23.2%), and trauma patterns.
2. Dry Eye Disease Epidemiology and Prevalence
Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Dry Eye Disease: Considerations for Clinical Management
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39336499/
Current research indicates a 10-20% prevalence in adults over 40, with detailed analysis of gender differences and risk factors affecting modern populations.
3. Digital Eye Strain and the 20-20-20 Rule Evidence
The effects of breaks on digital eye strain, dry eye, and binocular vision: Testing the 20-20-20 rule
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35963776/
A recent clinical study examined the effectiveness of scheduled breaks for digital eye strain relief and evidence-based recommendations for screen users.
Taking Action
If you’re currently experiencing red eye symptoms that concern you, don’t delay seeking appropriate evaluation. Early intervention consistently provides better outcomes while preventing the anxiety and complications associated with delayed care.
Ready to address your red eye concerns? Contact a Seattle-area optometrist today for comprehensive eye care that combines advanced diagnostics with personalized attention. Don’t let red eye symptoms affect your quality of life—professional help is available when you need it most.
Remember: your vision represents one of your most precious assets. When uncertainty exists about the significance of eye symptoms, professional evaluation provides the expertise needed to protect your sight and maintain optimal eye health throughout your lifetime.
This article provides general information about red eye conditions and should not replace professional medical advice. If you’re experiencing concerning eye symptoms, contact a qualified eye care professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
FAQs
-
Red eyes in one eye are commonly caused by episcleritis (inflammation), dry eye syndrome, allergies, or eye strain from screen time.