Ocular Rosacea
Bottom Line Up Front: Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory eye condition affecting the eyes and eyelids that can occur with or without facial rosacea. While there’s no cure, evidence-based treatments including warm compresses, omega-3 supplements, prescription medications, and innovative IPL therapy can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life when managed by experienced eye care professionals.
What is Ocular Rosacea? Understanding This Eye Condition
Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the eyes, eyelids, and surrounding skin. As one of the four recognized subtypes of rosacea, this eye condition can develop independently or alongside facial rosacea, often creating significant discomfort and visual disturbances for those affected.
Key Facts About Ocular Rosacea:
- Affects approximately 10-60% of people with facial rosacea (varying by study criteria)
- It can occur without any skin involvement in up to 20% of cases
- More common in adults aged 30-60, with peak incidence in 40s-60s
- Affects men and women equally (unlike facial rosacea, which affects more women)
- Often underdiagnosed due to subtle early symptoms
Understanding the Connection to Facial Rosacea
While ocular rosacea frequently accompanies the classic facial redness and bumps of traditional rosacea, it’s important to understand that these conditions can occur independently. Some people experience eye symptoms as their first sign of rosacea, while others may develop ocular involvement years after their skin symptoms begin.
The severity of ocular symptoms doesn’t always correlate with facial manifestations—patients with mild skin changes may experience significant eye problems, and vice versa.
Recognizing Ocular Rosacea Symptoms: Early Warning Signs
Early recognition of ocular rosacea symptoms is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining optimal eye health. The condition presents with a wide range of symptoms that can vary significantly between individuals and fluctuate over time.
Primary Eye-Related Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
Immediate Discomfort Symptoms:
- Burning, stinging, or gritty sensation in the eyes
- Persistent dry eye feeling despite adequate tear production
- Foreign body sensation (feeling like something is constantly in your eye)
- Eye redness and bloodshot appearance
- Excessive tearing or watery eyes
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Blurred vision or visual fluctuations
Progressive Symptoms:
- Recurrent styes or chalazia (eyelid bumps)
- Persistent eye fatigue, especially during computer work
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
- Morning eye discomfort that improves throughout the day
Eyelid and Surrounding Skin Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or inflamed eyelid margins
- Crusty discharge along the eyelashes
- Loss of eyelashes (madarosis) in severe cases
- Thickened or irregular eyelid margins
- Prominent blood vessels along the eyelid edges
Skin Changes Around the Eyes:
- Redness or discoloration around the eye area
- Swelling or puffiness of the eyelids
- Skin sensitivity or burning sensation
- Small papules or bumps on the eyelids
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
Ocular rosacea frequently involves dysfunction of the meibomian glands, which produce the oily layer of the tear film. This dysfunction leads to:
- Poor quality tears that evaporate quickly
- Clogged oil glands in the eyelids
- Thick, toothpaste-like secretions when glands are expressed
- Rapid tear film breakdown
Understanding the Causes of Ocular Rosacea: Latest Research Findings
The exact cause of ocular rosacea remains under investigation, but recent 2024-2025 research has identified several key factors that contribute to its development and progression.
Immune System Dysregulation
Current research suggests that ocular rosacea involves an overactive immune response, particularly affecting the innate immune system. Studies have identified:
- Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation leading to increased inflammatory signaling
- Complement system involvement causes chronic ocular surface inflammation
- Cytokine imbalances resulting in persistent inflammatory cascades
Genetic Factors
Recent research indicates that genetic predisposition plays a significant role in ocular rosacea development:
- Genome-wide association studies have identified specific genetic variations
- HLA associations (HLA-DRA, BTNLA2, HLA-DRB103:01) linked to increased risk
- Family history of rosacea increases the likelihood of developing ocular symptoms
- Genetic factors account for approximately 50% of rosacea susceptibility
Microbiome Disruption
Emerging research highlights the role of microbiome alterations in ocular rosacea:
- Demodex mites overgrowth on eyelash follicles and skin
- Bacterial imbalances on the ocular surface and eyelid margins
- Gut-eye axis dysfunction affecting overall inflammatory status
- Biofilm formation contributes to chronic inflammation
Vascular and Neurosensory Abnormalities
Ocular rosacea involves significant vascular and nerve-related changes:
- Abnormal blood vessel reactivity leading to flushing and redness
- Increased vascular permeability, causing tissue swelling
- Neurosensory dysfunction affecting pain and temperature sensation
- Oxidative stress contributes to ongoing tissue damage
Common Triggers of Ocular Rosacea Flare-ups: What to Avoid
Understanding and avoiding personal triggers is essential for managing ocular rosacea effectively. While triggers vary between individuals, research has identified several common categories that frequently cause symptom flare-ups.
Environmental Triggers
Weather and Climate:
- Hot, humid weather conditions
- Cold, windy environments
- Sudden temperature changes
- Direct sunlight exposure
- High altitude or low humidity environments
Indoor Environmental Factors:
- Dry indoor air from heating or air conditioning
- Poor air quality or pollution
- Smoke exposure (including secondhand smoke)
- Strong chemical odors or fragrances
Dietary Triggers
Common Food and Beverage Triggers:
- Spicy foods containing capsaicin
- Hot beverages (coffee, tea, hot chocolate)
- Alcohol, particularly red wine
- Aged cheeses and fermented foods
- Chocolate and caffeine-containing products
- Histamine-rich foods (aged meats, certain fish)
Individual Dietary Considerations:
- Food sensitivity varies significantly between people
- Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers
- Elimination diets may help pinpoint specific problematic foods
Lifestyle and Stress Factors
Physical Stressors:
- Intense physical exercise or overheating
- Sleep deprivation or irregular sleep patterns
- Hormonal fluctuations (menopause, menstrual cycles)
- Certain medications that affect blood vessels
Emotional and Mental Stressors:
- Work-related stress or deadline pressure
- Relationship or family conflicts
- Major life changes or traumatic events
- Anxiety and emotional intensity
Skincare and Cosmetic Triggers
Product-Related Triggers:
- Harsh skincare products containing alcohol or fragrances
- Certain makeup products, especially around the eye area
- Sunscreens with chemical UV filters
- Exfoliating products or aggressive cleansing routines
Current Treatment Options for Ocular Rosacea: Evidence-Based Approaches
Effective ocular rosacea management requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both symptoms and underlying inflammatory processes. Treatment strategies are typically implemented in stages based on severity and response to therapy.
First-Line Conservative Treatments
Lid Hygiene and Warm Compresses:
Conservative treatment forms the foundation of ocular rosacea management:
- Daily warm compresses (10-15 minutes, twice daily) help liquefy thickened meibomian gland secretions
- Gentle eyelid cleaning with diluted baby shampoo or specialized eyelid cleansers
- Lid massage following warm compresses to express blocked glands
- Artificial tears to supplement inadequate tear production
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Identifying and avoiding personal triggers
- Using humidifiers in dry environments
- Wearing wraparound sunglasses for UV and wind protection
- Implementing stress management techniques
Topical Prescription Treatments
- Cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion (Restasis, Cequa) – FDA-approved for dry eye, reduces inflammation, and improves tear production
- Lifitegrast (Xiidra) – blocks lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1, reducing the inflammatory cascade
- Tacrolimus ointment – calcineurin inhibitor for severe eyelid inflammation
Antibiotic Treatments:
- Azithromycin ophthalmic drops (AzaSite) – reduces bacterial load and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Metronidazole gel – antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects
- Erythromycin ointment – particularly useful for bacterial overgrowth
Oral Medications
Tetracycline-Class Antibiotics:
Research shows tetracyclines are highly effective for moderate to severe ocular rosacea:
- Doxycycline – most commonly prescribed, typically 40-100mg daily
- Minocycline – an alternative for doxycycline-intolerant patients
- Low-dose doxycycline (Oracea 40mg) – anti-inflammatory dose with reduced antibiotic resistance risk
Alternative Oral Treatments:
- Isotretinoin – reserved for severe, refractory cases due to side effect profile
- Omega-3 fatty acid supplements – emerging evidence for anti-inflammatory benefits
Advanced Treatment Options
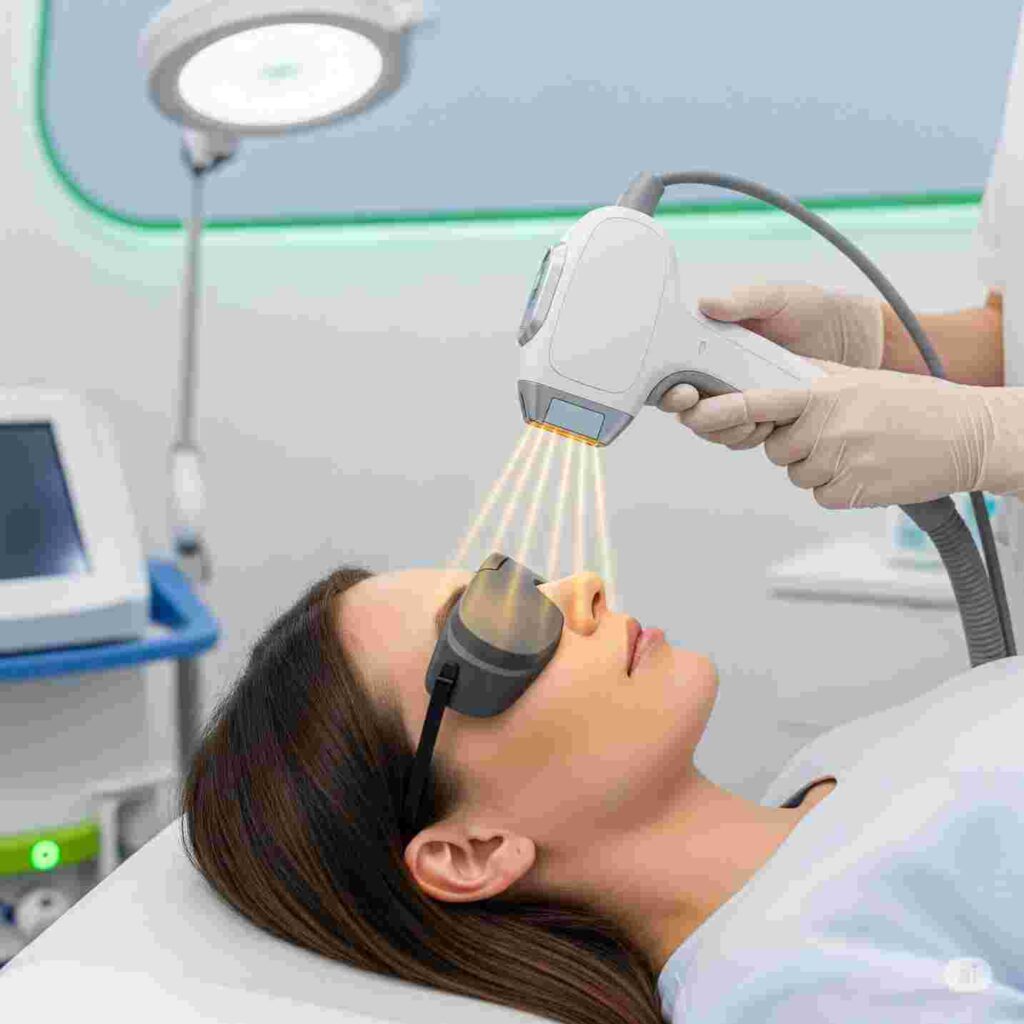
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy for Ocular Rosacea:
IPL has emerged as a promising treatment for ocular rosacea, particularly when combined with meibomian gland expression:
- Mechanism: Uses broad-spectrum light to reduce inflammation and target abnormal blood vessels
- Treatment protocol: Typically 3-4 sessions spaced 2-4 weeks apart
- Efficacy: Studies show 91% of patients experience partial symptom improvement
- Benefits: Reduces eyelid inflammation, improves meibomian gland function, minimal side effects
Specialized Procedures:
- Meibomian gland probing – mechanical opening of blocked glands
- LipiFlow treatment – thermal pulsation therapy for MGD
- BlephEx – in-office eyelid margin debridement
The Role of Omega-3 Supplements in Ocular Rosacea Treatment
Recent clinical research has provided compelling evidence for omega-3 fatty acids as an effective treatment option for ocular rosacea and associated dry eye symptoms.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Omega-3 Use
Clinical Trial Results:
A landmark randomized controlled trial involving 130 rosacea patients with dry eye symptoms found significant improvements with omega-3 supplementation:
- 325mg EPA and 175mg DHA twice daily for 6 months
- Significant improvement in subjective dry eye symptoms
- Enhanced meibomian gland function scores
- Improved tear film stability (TBUT)
- Better Schirmer test results
Mechanism of Action:
Omega-3 fatty acids benefit ocular rosacea through multiple pathways:
- Anti-inflammatory effects – reducing inflammatory cytokine production
- Improved meibomian gland health – enhancing oil quality and flow
- Stabilized tear film – better tear composition and reduced evaporation
- Reduced oxidative stress – protecting ocular surface tissues
Optimal Dosing and Recommendations
Evidence-Based Dosing:
- Minimum effective dose: 1000-1200mg combined EPA/DHA daily
- Optimal therapeutic dose: 325mg EPA + 175mg DHA twice daily (as demonstrated in clinical trials)
- Duration: Benefits are typically seen after 3-6 months of consistent use
- Quality considerations: Choose high-quality, molecularly distilled supplements
Patient Experiences:
According to patient reports, many experience:
- Reduced “sandpaper” feeling in eyes after 3-6 months
- Decreased frequency of dry eye episodes
- Improved comfort with computer work
- Better tolerance of environmental triggers
Living with Ocular Rosacea: Practical Daily Management Strategies
Successfully managing ocular rosacea requires developing comprehensive daily routines and long-term strategies that address both symptom management and trigger avoidance.
Daily Eye Care Routine
Morning Routine:
- Apply a warm compress for 10-15 minutes upon waking
- Gentle eyelid massage to express meibomian glands
- Clean eyelid margins with an appropriate cleanser
- Apply prescribed eye drops or ointments
- Use preservative-free artificial tears as needed
Evening Routine:
- Remove all eye makeup gently with a non-irritating remover
- Repeat warm compress and lid massage
- Apply overnight treatments as prescribed
- Use a bedroom humidifier for optimal moisture levels
Workplace and Digital Eye Strain Management
Computer Work Considerations:
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds
- Position the computer screen 20-26 inches away and slightly below eye level
- Use computer glasses with blue light filtering if helpful
- Maintain proper lighting to reduce glare and eye strain
- Take regular breaks to rest your eyes and reduce tear film evaporation
Travel and Environmental Management
Travel Preparation:
- Pack travel-sized eye care supplies
- Use airline-approved humidifiers or saline sprays
- Wear wraparound sunglasses for UV protection
- Stay hydrated and avoid known dietary triggers
- Plan for time zone changes that may affect medication schedules
When to Seek Professional Eye Care for Ocular Rosacea
Recognizing when to consult an eye care professional is crucial for preventing complications and optimizing treatment outcomes for ocular rosacea.
Urgent Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Vision-Threatening Signs:
- Sudden vision loss or significant vision changes
- Severe eye pain that doesn’t respond to usual treatments
- Signs of corneal involvement (severe light sensitivity, vision halos)
- Suspected eye infections with discharge or severe redness
- New onset of flashing lights or floating spots
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Recommended Follow-up Schedule:
- Initial diagnosis: follow-up within 2-4 weeks of starting treatment
- Stable patients: every 3-6 months for monitoring
- Treatment adjustments: 4-6 weeks after medication changes
- Annual comprehensive eye exams to monitor for complications
What to Discuss with Your Eye Doctor:
- Changes in symptom frequency or severity
- Response to current treatments
- New triggers or lifestyle factors
- Interest in advanced treatment options like IPL
- Impact on daily activities and quality of life
Recent Research and Future Directions in Ocular Rosacea Treatment
The field of ocular rosacea research is rapidly evolving, with new insights into pathophysiology and innovative treatment approaches emerging from 2024-2025 studies.
Cutting-Edge Research Findings
Microbiome Research: Recent studies have revealed important connections between ocular surface microbiome and rosacea symptoms:
- Specific bacterial species associated with symptom severity
- Potential for targeted probiotic treatments
- Role of gut microbiome in systemic inflammation
Genetic Studies: New genetic research is providing insights into:
- Personalized treatment approaches based on genetic markers
- Inherited susceptibility patterns
- Potential gene therapy targets for the future
Advanced Imaging Studies: Modern imaging techniques are revealing:
- Real-time meibomian gland function assessment
- Inflammatory marker tracking
- Objective measures of treatment response
Emerging Treatment Modalities
Novel Therapies in Development:
- Targeted anti-inflammatory medications with fewer side effects
- Advanced light-based therapies combining multiple wavelengths
- Regenerative treatments for damaged meibomian glands
- Precision medicine approaches based on individual inflammatory profiles
Technology Integration:
- Smartphone apps for trigger tracking and symptom monitoring
- Telemedicine consultations for ongoing management
- AI-powered treatment optimization algorithms
References and Additional Resources
Key Clinical Studies and Research
1. Ocular Rosacea: An Updated Review (2025) Mohamed-Noriega K, et al. Cornea. 2025 Apr 1;44(4):525-537 This comprehensive 2025 review provides the latest understanding of ocular rosacea pathogenesis, including immune dysregulation mechanisms and emerging therapeutic targets. Essential reading for understanding current treatment approaches and future directions in ocular rosacea management. 📖 Read Full Study on PubMed 📄 Access PDF via PMC
2. Treatment of Ocular Rosacea: A Systematic Review (2024) Avraham S, et al. JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 2024 Jan 20 This systematic review analyzed 66 articles representing 1,275 patients to compare treatment efficacy across different modalities. Key findings include 91% success rates for topical antimicrobials and comprehensive IPL therapy outcomes. Critical resource for evidence-based treatment decisions. 📖 Read Full Study 📊 View Treatment Comparison Data
3. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Omega 3 Fatty Acids in Rosacea Patients (2016) Bhargava R, et al. Current Eye Research. 2016;41(10):1274-1280 This landmark randomized controlled trial of 130 rosacea patients established the evidence base for omega-3 supplementation in ocular rosacea. The study demonstrated significant improvements with 325mg EPA and 175mg DHA twice daily for 6 months, providing the foundation for current nutritional therapy recommendations. 📖 Read Full Study on PubMed 📄 Access Complete Trial Data
Additional Professional Resources
National Rosacea Society: Comprehensive patient education materials and latest research updates on all rosacea subtypes, including ocular manifestations. 🌐 Visit NRS Website 📚 Ocular Rosacea Information
American Academy of Ophthalmology – Ocular Rosacea Facts: Professional guidelines and patient education resources from the leading eye care organization. 🌐 AAO Ocular Rosacea Guide
Conclusion: Managing Ocular Rosacea Successfully in 2025
Ocular rosacea is a complex, chronic condition that requires comprehensive management and ongoing attention. While there is no cure, the combination of proper diagnosis, individualized treatment plans, and consistent self-care can lead to significant symptom improvement and enhanced quality of life.
Essential Points to Remember:
- Early recognition and professional eye care prevent complications and vision problems
- Trigger identification and avoidance form the foundation of successful management
- Multiple evidence-based treatment options exist, from basic lid hygiene to advanced IPL therapy
- Omega-3 supplements (325mg EPA + 175mg DHA twice daily) provide clinically proven benefits
- Regular follow-up with experienced eye care professionals ensures optimal outcomes
Taking Action for Your Eye Health: If you’re experiencing persistent eye discomfort, dryness, or irritation, especially if you have a history of facial rosacea, don’t wait to seek professional evaluation. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most people with ocular rosacea can achieve significant symptom relief and maintain excellent eye health throughout their lives.
The key to success lies in working closely with experienced eye care professionals who understand the complexities of ocular rosacea and can develop personalized treatment strategies that address your specific symptoms, triggers, and lifestyle needs.
FAQs
-
Ocular rosacea is an inflammatory condition causing eye redness, burning, itching, and dryness. It affects eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea, often occurring with facial rosacea symptoms.