Eye Movement
What Is Eye Movement?
Eye movement encompasses both voluntary and involuntary movements that allow your eyes to track objects, maintain visual stability, and gather information from your environment. These sophisticated movements occur thousands of times daily, coordinating seamlessly with your brain to create the stable, detailed vision you experience.
Key Functions of Eye Movement:
- Maintaining a clear focus on moving objects
- Scanning environments for important information
- Coordinating binocular vision between both eyes
- Compensating for head and body movements
- Supporting depth perception and spatial awareness
Eye movements serve as a window into neurological health, cognitive function, and visual processing capabilities. Understanding these movements helps identify potential issues early and optimize visual performance throughout life.
The Six Essential Types of Eye Movements
Modern research identifies six distinct categories of eye movements, each serving specific visual functions and controlled by different neural pathways.
1. Saccadic Eye Movements
Definition: Rapid, ballistic movements that quickly shift gaze between fixation points.
Characteristics:
- Speed ranges from 30-500 degrees per second
- Duration typically 20-100 milliseconds
- Vision is temporarily suppressed during movement
- Cannot be consciously modified once initiated
Daily Applications:
- Reading text across a page
- Scanning a room for objects
- Looking between distant and near targets
- Navigating complex visual environments
2. Smooth Pursuit Movements
Definition: Slower, controlled movements that track moving objects.
Key Features:
- Maximum velocity is around 30 degrees per second
- Require a moving target to function optimally
- Can be consciously controlled to some degree
- Essential for following moving objects
Real-World Examples:
- Watching a ball during sports
- Following a car while driving
- Tracking falling objects
- Observing moving wildlife
3. Vergence Movements
Definition: Coordinated movements that adjust the angle between both eyes for depth perception.
Types:
- Convergence: Eyes move inward for near objects
- Divergence: Eyes move outward for distant objects
Critical Functions:
- Maintaining a single, clear vision at different distances
- Supporting stereoscopic depth perception
- Preventing double vision
- Facilitating a comfortable near work
4. Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex (VOR)
Definition: Automatic eye movements that compensate for head motion.
Mechanism:
- Detects head movement via the inner ear
- Generates opposite eye movement within 7-15 milliseconds
- Maintains stable vision during head movements
- Functions without conscious control
Importance:
- Stabilizes vision while walking or running
- Prevents motion blur during activities
- Supports balance and spatial orientation
- Critical for navigation and mobility
5. Optokinetic Movements
Definition: Eye movements responding to large-scale visual motion.
Function:
- Tracks slowly moving visual patterns
- Complements the vestibulo-ocular reflex
- Helps maintain visual stability
- Responds to environmental motion cues
6. Fixational Eye Movements
Definition: Microscopic movements occurring during apparent visual fixation.
Components:
- Microsaccades: Small, rapid jerks
- Tremor: High-frequency oscillations
- Drift: Slow, wandering movements
Purpose:
- Prevents visual fading (perceptual adaptation)
- Maintains optimal retinal stimulation
- Supports fine visual discrimination
- Enhances edge detection and contrast sensitivity
The Anatomy Behind Eye Movement Control
Understanding eye movement requires knowledge of the intricate muscular and neural systems that coordinate these precise movements.
Extraocular Muscles: The Movement Engine
Six Muscles Per Eye:
- Lateral Rectus: Moves the eye outward (abduction)
- Medial Rectus: Moves the eye inward (adduction)
- Superior Rectus: Elevates and slightly rotates the eye
- Inferior Rectus: Depresses and slightly rotates the eye
- Superior Oblique: Primary rotator, also depresses when the eye is adducted
- Inferior Oblique: Elevates when the eye is adducted, and contributes to rotation
Neural Control Centers
Cranial Nerves:
- Oculomotor Nerve (CN III): Controls four of six muscles per eye
- Trochlear Nerve (CN IV): Controls the superior oblique muscle
- Abducens Nerve (CN VI): Controls the lateral rectus muscle
Brain Regions:
- Frontal Eye Fields: Voluntary saccade generation
- Parietal Cortex: Spatial attention and saccade targeting
- Brainstem Nuclei: Pattern generation and coordination
- Cerebellum: Fine-tuning and adaptation
- Vestibular System: Balance and reflex coordination
How Eye Movements Impact Daily Vision and Performance
Eye movements directly influence visual performance, reading efficiency, sports performance, and overall quality of life.
Reading and Academic Performance
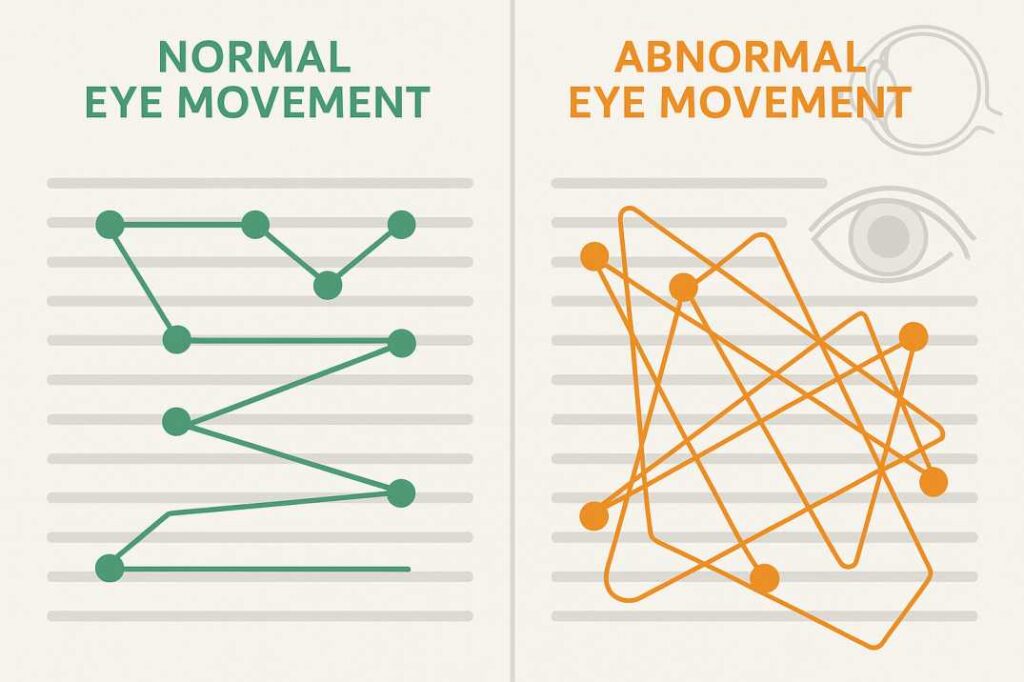
Optimal Reading Patterns:
- Forward saccades of 7-9 character spaces
- Fixation durations of 200-250 milliseconds
- Minimal regression (backward) movements
- Efficient return sweeps to new lines
Signs of Reading Difficulties:
- Excessive regressions or re-reading
- Irregular saccade patterns
- Prolonged fixation durations
- Frequent loss of place
Sports and Athletic Performance
Critical Skills:
- Rapid target acquisition and tracking
- Peripheral vision awareness
- Hand-eye coordination integration
- Anticipatory eye movements
Sport-Specific Demands:
- Baseball/Cricket: Tracking fast-moving balls
- Tennis: Following the ball trajectory and opponent position
- Basketball: Peripheral awareness and depth judgment
- Driving: Scanning traffic and hazard detection
Workplace Visual Demands
Computer Work Considerations:
- Vergence flexibility for multiple screen distances
- Efficient scanning patterns for complex interfaces
- Reduced blink rates requiring conscious attention
- Blue light exposure effects on circadian rhythms
Professional Applications:
- Surgery: Precise hand-eye coordination
- Air Traffic Control: Rapid target identification
- Quality Inspection: Systematic visual scanning
- Teaching: Dynamic visual presentation skills
Eye Movement Disorders: Recognition and Understanding
Eye movement disorders can significantly impact daily function and may indicate underlying neurological conditions.
Common Movement Disorders
Nystagmus
Definition: Involuntary, rhythmic eye movements that can be horizontal, vertical, or rotational.
Types:
- Congenital: Present from birth, often horizontal
- Acquired: Develops later, may indicate neurological issues
Symptoms:
- Blurred or shaky vision
- Head tilting to find “null point”
- Reduced visual acuity
- Balance difficulties
Management Options:
- Corrective lenses with prisms
- Contact lenses for some types
- Medications (limited effectiveness)
- Surgery in select cases
Strabismus (Eye Misalignment)
Definition: A Condition where the eyes don’t align properly, affecting binocular vision.
Types:
- Esotropia: Inward turning
- Exotropia: Outward turning
- Hypertropia: Upward deviation
- Hypotropia: Downward deviation
Treatment Approaches:
- Vision therapy exercises
- Corrective lenses with prisms
- Surgical realignment
- Botulinum toxin injections
Cranial Nerve Palsies
Definition: Weakness or paralysis of eye movement muscles due to nerve damage.
Common Causes:
- Diabetes complications
- Head trauma
- Vascular incidents
- Increased intracranial pressure
Symptoms:
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Limited eye movement range
- Head tilting or turning
- Difficulty with specific gaze directions
Warning Signs Requiring Professional Evaluation
Immediate Attention Needed:
- Sudden onset of double vision
- Severe eye movement limitations
- Persistent dizziness with eye symptoms
- Vision loss accompanied by movement changes
Gradual Changes to Monitor:
- Increasing difficulty reading
- Frequent headaches during visual tasks
- Eye strain or fatigue
- Changes in depth perception
Diagnostic Applications and Modern Testing Methods
Advanced diagnostic techniques allow precise evaluation of eye movement function and early detection of disorders.
Traditional Clinical Assessment
Cover Test:
- Evaluates eye alignment and coordination
- Detects latent eye turn tendencies
- Assesses binocular vision stability
- Monitors treatment progress
Smooth Pursuit Testing:
- Patient tracks a slowly moving target
- Evaluates pursuit accuracy and smoothness
- Identifies neurological dysfunction
- Assess visual-motor integration
Saccade Assessment:
- Rapid eye movement evaluation
- Test accuracy and speed
- Identifies cerebellar or brainstem issues
- Measures cognitive processing speed
Advanced Technological Methods
Video-Oculography (VOG)
Capabilities:
- Precise movement measurement in three dimensions
- Quantitative analysis of all movement types
- Objective documentation of abnormalities
- Treatment monitoring over time
Applications:
- Vestibular disorder diagnosis
- Neurological condition assessment
- Concussion evaluation protocols
- Athletic performance optimization
Eye Tracking Technology
Research Applications:
- Reading pattern analysis through advanced eye tracking
- Cognitive load assessment
- User interface design optimization
- Educational effectiveness measurement
Clinical Potential:
- Early autism spectrum detection
- ADHD assessment support
- Alzheimer’s disease monitoring
- Psychiatric condition evaluation
Emerging Diagnostic Innovations
Smartphone-Based Testing:
- Accessible screening tools
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Cost-effective population screening
- Telemedicine integration potential
AI-Assisted Analysis:
- Pattern recognition algorithms
- Automated abnormality detection
- Predictive modeling capabilities
- Personalized treatment recommendations
Recent Scientific Breakthroughs in Eye Movement Research
Current research reveals new insights into eye movement functions and clinical applications.
2024-2025 Research Highlights
Smartphone Eye Tracking Validation
Recent studies demonstrate that smartphone-based eye tracking achieves accuracy comparable to traditional research-grade equipment. This breakthrough enables widespread access to eye movement assessment, particularly valuable for:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Population-level screening programs
- Educational research in diverse settings
- Accessibility improvements for underserved communities
Eye Movements and Autism Detection
Researchers at UC San Francisco discovered that children with specific genetic variants (SCN2A gene) associated with autism demonstrate unusual vestibulo-ocular reflex patterns. This finding suggests potential for:
- Earlier autism spectrum detection
- Objective diagnostic support tools
- Genetic variant impact assessment
- Personalized intervention planning
Environmental Attention and Well-being
A comprehensive study using mobile eye tracking revealed that directing visual attention toward natural elements (trees, water, sky) significantly improves psychological well-being compared to focusing on human-made structures. Implications include:
- Urban planning considerations
- Therapeutic environment design
- Stress reduction strategies
- Biophilic design validation
Technological Advances
Event-Based Eye Tracking:
- Ultra-high speed capture (up to 300 degrees/second)
- Reduced power consumption for wearable devices
- Enhanced accuracy for rapid movement detection
- Applications in gaming and virtual reality
Multimodal Integration:
- Combining eye tracking with EEG, fMRI, and physiological measures
- Comprehensive cognitive state assessment
- Real-time adaptation systems
- Enhanced research methodology validation
Eye Movement Training and Vision Therapy Options
Various therapeutic approaches can improve eye movement function and overall visual performance.
Vision Therapy Exercises
Saccadic Training
Exercises:
- Hart Chart: Alternating focus between near and far targets
- Number Tracking: Following sequences of numbers or letters
- Computer-Based Programs: Adaptive difficulty training systems
- Sports Vision Drills: Activity-specific movement patterns
Benefits:
- Improved reading speed and comprehension
- Enhanced sports performance
- Reduced eye strain during computer work
- Better visual attention and concentration
Pursuit Enhancement
Training Methods:
- Circle Tracking: Following circular or figure-8 patterns
- Pendulum Exercises: Smooth tracking of swinging objects
- Video Game Integration: Motion-tracking gameplay
- Real-World Practice: Ball sports and moving object activities
Vergence Development
Therapeutic Approaches:
- Convergence Exercises: Pencil push-ups and similar techniques
- Divergence Training: Distance fixation exercises
- Computer Programs: Binocular coordination software
- Prism Adaptation: Graduated prism lens training
Professional Treatment Options
Optometric Vision Therapy
Components:
- Comprehensive eye movement assessment
- Individualized exercise programs
- Progress monitoring and adjustment
- Integration with educational or occupational needs
Duration and Expectations:
- Typical programs: 12-24 weeks
- Session frequency: 1-2 times weekly
- Home exercise components
- Measurable improvement tracking
Occupational Therapy Integration
Applications:
- Coordination with motor skill development
- Functional task integration
- Adaptive strategy development
- Environmental modification recommendations
Technology-Enhanced Training
Virtual Reality Applications:
- Immersive training environments
- Precise movement tracking and feedback
- Gamified exercise programs
- Customizable difficulty progression
Smartphone Apps:
- Accessible daily training options
- Progress tracking capabilities
- Reminder and motivation systems
- Professional monitoring integration
Maintaining Optimal Eye Movement Health
Prevention and maintenance strategies support lifelong eye movement function and visual comfort.
Daily Habits for Eye Movement Health
Digital Device Guidelines:
- 20-20-20 Rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds
- Screen Positioning: Top of screen at or below eye level
- Lighting Optimization: Reduce glare and provide adequate ambient lighting
- Blink Awareness: Conscious complete blinking to maintain the tear film
Physical Activity Benefits:
- Sports Participation: Natural eye movement training
- Outdoor Time: Distance vision anthe d natural light exposure
- Balance Exercises: Support vestibular-ocular integration
- Head Movement Activities: Maintain reflex coordination
Nutritional Support
Key Nutrients:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Support tear production and neural function
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Protect retinal tissues
- Vitamin A: Essential for photoreceptor function
- Antioxidants: Reduce oxidative stress in neural tissues
When to Seek Professional Care
Regular Eye Examinations:
- Annual comprehensive eye exams
- Discussion of visual symptoms or changes
- Eye movement assessment inclusion
- Early intervention when needed
Specialist Referral Indicators:
- Persistent double vision
- Difficulty with reading or close work
- Frequent headaches with visual tasks
- Changes in depth perception or coordination
Scientific References and Additional Resources
This article draws from current peer-reviewed research and authoritative medical sources. The following key references provide additional depth for readers interested in the scientific foundations of eye movement research:
Primary Research Sources
1. Types of Eye Movements and Their Functions – NCBI Neuroscience
National Center for Biotechnology Information
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10991/
This comprehensive neuroscience textbook chapter provides detailed explanations of the four basic types of eye movements: saccades, smooth pursuit, vergence, and vestibulo-ocular movements. Essential reading for understanding the neural circuitry and functional mechanisms behind each movement type.
2. Accelerating Eye Movement Research via Accurate and Affordable Smartphone Eye Tracking
Nature Communications, 2020
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-18360-5
Groundbreaking research demonstrates that smartphone-based eye tracking achieves accuracy comparable to traditional research-grade equipment. This study validates the potential for democratizing eye movement assessment and expanding access to diagnostic capabilities.
3. Could We Assess Autism in Children With a Simple Eye Reflex Test?
UC San Francisco, 2024
https://www.ucsf.edu/news/2024/02/427171/could-we-assess-autism-children-simple-eye-reflex-test
Recent breakthrough research shows that children with SCN2A gene variants associated with autism demonstrate unusual vestibulo-ocular reflex patterns, suggesting potential for earlier and more objective autism spectrum detection methods.
Conclusion: The Future of Eye Movement Understanding
Eye movement research continues evolving rapidly, with new technologies and insights expanding our understanding of these fundamental visual processes. From smartphone-based screening tools to AI-assisted diagnosis, the future promises more accessible, precise, and comprehensive eye movement assessment.
Understanding your eye movements empowers you to recognize potential issues early, optimize visual performance, and maintain lifelong eye health. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms, seeking performance enhancement, or simply curious about how your visual system works, this knowledge provides valuable insights into one of your body’s most sophisticated and essential functions.
Key Takeaways:
- Eye movements are complex, coordinated processes essential for daily function.
- Six distinct movement types serve specific visual purposes
- Early detection of movement disorders can significantly improve.e outcomes
- Technology continues to expand access to sophisticated assessment tools
- Simple daily habits can support optimal eye movement to expand throughout life
For personalized assessment and care recommendations, consult with qualified eye care professionals who can evaluate your individual eye movement patterns and visual needs. At Cannon EyeCare, we provide comprehensive eye movement evaluations that combine the latest diagnostic technology with personalized care, serving the Seattle community from our convenient University Village and Pike Place Market locations.
This article provides educational information based on current scientific literature and clinical practice standards. The content should not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Individuals experiencing vision concerns or eye movement abnormalities should consult qualified healthcare providers for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations. For appointments and specialized consultations in the Seattle metropolitan area, contact Cannon EyeCare.
FAQs
-
Eye “glitching” occurs when eye muscles experience temporary spasms or struggle to maintain proper focus, often caused by eye strain, fatigue, or accommodative dysfunction requiring professional evaluation