Understanding 3D Vision: Movies, Health & Technology
Introduction: The Revolutionary World of 3D Cinema
Three-dimensional cinema has transformed from a novelty attraction into a sophisticated entertainment medium that captivates audiences worldwide. From the early red-and-blue anaglyph glasses of the 1950s to today’s advanced polarized technology and cutting-edge VR headsets, 3D vision and movies continue to evolve together, pushing the boundaries of immersive storytelling.
Understanding how 3D movies work, their impact on our visual system, and the latest technological advances empowers viewers to make informed decisions about their entertainment choices and eye health. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate relationship between 3D vision and movies, examining the science behind stereoscopic technology, modern cinema innovations, potential health considerations, and the promising future of three-dimensional entertainment.
The Science Behind 3D Vision and Movies
The Foundation of Human Depth Perception
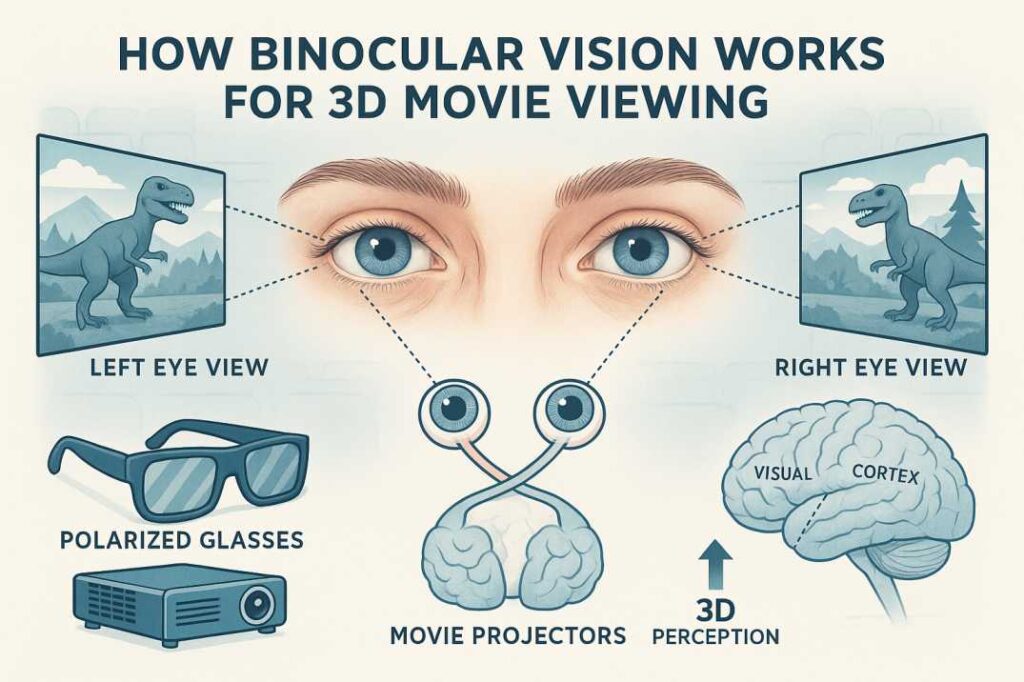
Human depth perception relies on binocular vision—a sophisticated biological process where each eye captures the world from a slightly different perspective. Separated by approximately 5 centimeters, our eyes create two distinct images that our brain seamlessly processes and triangulates to determine object distance and spatial relationships.
This natural stereoscopic capability forms the foundation for all 3D movie technology. Cinema engineers replicate this biological process using specialized cameras with dual lenses positioned to mimic human eye spacing. This technological recreation of our visual system’s natural depth perception enables the three-dimensional illusions we experience in theaters and at home.
Modern 3D Movie Technology Methods
Polarized Light Technology
Contemporary 3D cinema primarily employs polarization technology, the most sophisticated and widely adopted method. This system projects two simultaneous images onto the same screen, each polarized in different orientations. Viewers wear specially designed glasses with polarized lenses—one filtering horizontal light waves, the other vertical waves—ensuring each eye receives only its intended image.
Polarized 3D glasses function similarly to polarized sunglasses, selectively filtering light from specific directions. This method significantly surpasses older anaglyph systems because it preserves full color reproduction and accommodates viewers with color vision deficiencies.
Active Shutter Technology
Higher-end applications utilize LCD shutter glasses that rapidly alternate between transparent and opaque states, synchronized with alternating left-eye and right-eye images displayed at high refresh rates. Television manufacturers primarily implement this technology for home 3D systems, though it requires more expensive equipment and precise timing.
Legacy Anaglyph Method
The historical red-and-blue anaglyph method, pioneered in films like “The Power of Love” (1922), represents the earliest widespread 3D technology. While limited by color distortion and reduced visual quality, this approach established the foundational principles still used in modern systems.
Evolution of 3D Movies: From Historical Novelty to Modern Entertainment
Early 3D Cinema History
The first 3D film, “L’Arrivée du Train” (1903), demonstrated such convincing realism that audiences reportedly ducked to avoid the oncoming locomotive. This French short film established 3D cinema’s potential for unprecedented immersion, though technical limitations prevented widespread adoption for decades.
The 1950s witnessed 3D cinema’s first commercial peak with “Bwana Devil” (1952) and subsequent action films. However, poor production quality and viewer discomfort led to rapid decline, establishing a pattern of boom-and-bust cycles that would characterize 3D cinema for decades.
The Modern 3D Revival
Computer-generated imagery revolutionized 3D cinema in the early 21st century. Films like “The Polar Express” (2004) and “Coraline” (2009) demonstrated 3D’s artistic potential, but James Cameron’s “Avatar” (2009) truly transformed the medium. This groundbreaking film proved that sophisticated 3D technology could enhance storytelling while achieving unprecedented commercial success.
Current State of 3D Cinema
Recent industry data reveals 3D cinema’s remarkable recovery following the global pandemic. In 2023, films released in both 2D and 3D formats earned $6.5 billion globally, with $1.7 billion generated specifically from 3D ticket sales—a post-pandemic record according to RealD analytics.
The domestic take rate demonstrates improving audience acceptance: live-action 3D titles increased from 11.5% in 2019 to 14.9% in 2023, while animated 3D features rose from 6.8% to 11.3% during the same period. This resurgence indicates renewed consumer confidence in high-quality 3D entertainment.
Apple Vision Pro and the Future of 3D Movies
Revolutionary Home 3D Experience
Apple’s Vision Pro represents a paradigm shift in home entertainment, launching with over 150 3D movies from major studios, including “Avatar: The Way of Water,” “Dune,” and “Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse.” Priced starting at $3,499, the device provides theatrical-quality 3D experiences that many reviewers claim surpass traditional cinema presentations.
The platform offers unprecedented accessibility, with users accessing 3D versions of purchased movies at no additional cost. Disney+ provides over 40 3D titles specifically optimized for Vision Pro, while Apple TV+ features hundreds of additional 3D movies, creating the most comprehensive home 3D library ever assembled.
Apple Immersive Video Technology
Apple Immersive Video introduces a proprietary format featuring 180-degree 3D 8K recordings captured with Spatial Audio technology. This innovation delivers more pixels than a 4K television to each eye, combined with advanced spatial audio processing that creates truly immersive experiences impossible with traditional displays.
Health Effects of 3D Vision and Movies
The relationship between 3D vision and movies has evolved dramatically since cinema’s early days. Understanding this connection helps viewers appreciate both technological achievements and potential health considerations associated with three-dimensional entertainment.
Understanding Potential Side Effects
Comprehensive research provides clear data on 3D viewing effects. A rigorous study involving 497 healthy adults found that 54.8% of participants reported some discomfort after experiencing 3D vision and movies, compared to only 14.1% after traditional 2D presentations. Symptom intensity measured 8.8 times higher following 3D exposure, with women showing particular susceptibility to visual-vestibular effects.
Common Symptoms and Their Causes
The most frequently reported symptoms during or after 3D movie viewing include headaches, blurred vision, fatigue, and nausea. These effects occur when the brain struggles to combine disparate images from each eye, working harder to create unified, comfortable vision. This complex relationship between 3D vision and movies continues to be studied by vision researchers worldwide.
3D technology requires eye muscles to function in unfamiliar patterns, potentially causing eye strain and headaches. Rapid scene changes during this adjustment period may trigger dizziness and nausea. Fortunately, these symptoms typically resolve quickly once viewing stops, with no documented long-term effects.
Medical Safety Assessments
Leading medical organizations provide reassuring guidance about 3D safety. The American Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus and the American Academy of Ophthalmology report no known studies demonstrating long-term vision damage from 3D entertainment. Ophthalmologists consistently state that 3D movies, television, and video games pose no significant risk to visual system health.
Professional medical consensus confirms that 3D viewing is safe, though individual tolerance varies significantly based on underlying vision characteristics and viewing duration.
Who May Experience Difficulties with 3D Movies
Binocular Vision Disorders
Certain vision conditions significantly impact 3D perception capabilities. Amblyopia, commonly called “lazy eye,” occurs when one eye provides substantially weaker visual input than the other. The brain compensates by suppressing information from the weaker eye, effectively eliminating binocular vision and depth perception necessary for 3D viewing.
Research indicates that approximately 12% of the population cannot perceive 3D images due to various medical conditions, while up to 30% experience significantly reduced stereoscopic vision that limits depth perception based on binocular disparity.
Vision Conditions Affecting 3D Perception
Specific populations face particular challenges with 3D entertainment. About 5% of people rely primarily on monocular vision (single-eye dominance), making 3D perception impossible. An additional 25% have borderline binocular vision, meaning they can theoretically perceive 3D but find the experience difficult or uncomfortable.
Conditions that commonly interfere with 3D viewing include:
- Strabismus (eye misalignment)
- Convergence insufficiency (difficulty focusing on near objects)
- Uncorrected refractive errors (nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism)
- Previous eye surgeries affecting muscle coordination
When to Consult an Eye Care Professional
If you regularly experience eye strain from watching 3D movies, consult an eye doctor. Underlying vision issues, such as uncorrected refractive errors or binocular vision problems, might be contributing factors that can be diagnosed and treated.
Eye care professionals like those at specialized practices such as Cannon EyeCare in Seattle are increasingly using 3D presentations and therapies to measure eyesight accuracy and detect binocular vision problems. These comprehensive evaluations can help determine if 3D viewing difficulties indicate underlying conditions like amblyopia, strabismus, or convergence insufficiency that may benefit from vision therapy or corrective treatment.
Recent Scientific Research on 3D Vision and Movies
Therapeutic Potential for Vision Problems
Groundbreaking 2024 research reveals unexpected therapeutic benefits of 3D movie viewing. A carefully controlled pilot study found that children with previously treated amblyopia experienced significant improvements in visual acuity and stereoscopic depth perception after watching a single 110-minute 3D movie in cinema conditions.
Most remarkably, these improvements persisted for at least three months following the single viewing session. This research suggests that exposure to large binocular disparities during 3D movie viewing may stimulate visual development in ways that traditional vision therapy approaches cannot replicate.
Vision Screening Applications
Modern optometry increasingly incorporates 3D technology into diagnostic procedures. These presentations require precise coordination between both eyes and the brain’s visual processing centers, making them excellent screening tools for detecting binocular vision disorders that might otherwise go unnoticed during routine examinations.
3D viewing difficulties often serve as early indicators of treatable conditions, allowing eye care professionals to intervene before problems significantly impact daily activities or academic performance.
Tips for Comfortable 3D Movie Viewing
Reducing Symptoms and Discomfort
Several evidence-based strategies minimize potential discomfort during 3D viewing:
Take Regular Breaks: Rest your eyes every 20-30 minutes by looking away from the screen and focusing on distant objects to relax accommodative muscles.
Maintain Optimal Viewing Distance: Position yourself approximately two to three times the screen height away from the display to reduce excessive convergence demands.
Start Gradually: Begin with shorter viewing sessions before attempting full-length features, allowing your visual system to adapt progressively.
Focus Strategically: Concentrate on main action elements rather than blurred background details, which can confuse the brain’s depth processing mechanisms.
Consider Vision Therapy: If problems persist, consult with developmental optometrists who specialize in binocular vision disorders and can provide targeted therapeutic interventions.
Professional Evaluation Benefits
Regular eye examinations become particularly important for frequent 3D viewers. Underlying refractive errors, muscle imbalances, or convergence insufficiencies that cause minimal problems during normal activities may become significantly symptomatic during 3D viewing, providing valuable diagnostic information about visual system function.
The Future of 3D Vision and Movie Technology
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Computer vision technology continues advancing rapidly, with key developments for 2025 including edge computing for faster image processing, enhanced 3D modeling algorithms for realistic visualizations, and improved data annotation techniques for machine learning applications. These innovations directly impact 3D entertainment quality and accessibility.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Integration
Rapid development in 3D reconstruction technology, including neural radiance fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS), creates increasingly sophisticated immersive experiences. Major technology companies, including Apple, Meta, Google, and Sony, continue investing heavily in AR/VR platforms that promise to revolutionize entertainment consumption.
Future Apple Vision Pro Models
Industry analysts report that Apple may release a more affordable Vision Pro model in 2025, priced around $2,000 compared to the current $3,499 starting price. This lower-cost version would utilize less powerful processors and more plastic construction materials while removing features like the EyeSight external display.
Apple is reportedly developing updated Vision Pro models with chip upgrades from M2 to M4 or M5 processors in 2025, with a completely redesigned second-generation device potentially launching in late 2027 or 2028, featuring reduced weight and enhanced performance.
Practical Considerations for 3D Movie Enthusiasts
Choosing the Right 3D Experience
When selecting 3D entertainment options, consider several key factors:
Viewing Environment: Modern home 3D technology, particularly Apple Vision Pro, often provides superior experiences compared to traditional theater presentations, offering personalized optimization and eliminating external distractions.
Content Quality: Films originally shot with stereoscopic cameras typically deliver better visual quality than post-production conversions from 2D source material.
Personal Tolerance: Individual sensitivity to 3D effects varies dramatically, making personal experimentation essential for determining optimal viewing parameters.
Session Duration: Shorter content may prove more comfortable for viewers sensitive to 3D effects, allowing gradual adaptation over time.
Investment Considerations
While 3D entertainment experiences have cyclical popularity, underlying technology continues evolving and integrating across televisions, projectors, streaming platforms, and mobile devices. Blu-ray 3D remains the preferred format among enthusiasts, offering superior visual and audio quality compared to compressed streaming alternatives.
Specialized companies like 3D Film Archive continue restoring vintage stereoscopic films, while boutique labels produce original 3D content, ensuring the continued availability of high-quality materials for dedicated enthusiasts.
Resources and Citations
The following peer-reviewed studies and authoritative sources provide the scientific foundation for the health effects and research findings discussed in this article:
1. Scientific Study on 3D Movie Side Effects
Solimini, A. G. (2013). “Are there side effects to watching 3D movies? A prospective crossover observational study on visually induced motion sickness.” PLOS ONE, 8(2), e56160.
- Key Finding: Study of 497 healthy adults found 54.8% experienced sickness after 3D movies vs 14.1% after 2D movies, with 8.8 times higher symptom intensity
- Relevance: Provides the primary statistical data on 3D movie health effects cited throughout the article
- Access: PubMed | PLOS ONE Open Access
2. Recent Research on Therapeutic Applications
Asensio-Jurado, L., Argilés, M., Quevedo-Junyent, L., Mestre, C., & Levi, D. M. (2024). “Can viewing a 3D movie improve visual function in children with a history of amblyopia and neurotypical children?: A pilot study.” PLOS ONE, 19(6), e0305401.
- Key Finding: 110-minute 3D movie viewing improved visual acuity and stereoscopic depth perception in children with amblyopia, with effects lasting 3 months
- Relevance: Demonstrates potential therapeutic benefits of 3D movie viewing for certain vision conditions
- Access: PubMed | PLOS ONE Open Access
3. Industry Analysis and Market Data
Variety Staff. (2024, June 14). “Summer Movie Season Testing 3D Cinema’s Recoverability.” Variety.
- Key Finding: 2023 global box office data showing $6.5 billion total for 2D/3D films, with $1.7 billion from 3D ticket sales representing a post-pandemic record
- Relevance: Provides current market statistics and industry trends for 3D cinema performance
- Access: Variety Entertainment Industry Analysis
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of 3D Vision and Movies
The relationship between 3D vision and movies continues evolving rapidly, offering increasingly sophisticated and immersive entertainment experiences. Current medical evidence confirms that enjoying 3D vision and movies remains safe for most viewers when approached responsibly and with awareness of individual limitations.
Understanding your personal vision characteristics, recognizing potential symptoms, and implementing appropriate viewing strategies ensures positive experiences with 3D vision and movies. For individuals with underlying vision conditions, professional consultation provides personalized guidance and may reveal treatable problems that improve both 3D viewing comfort and general visual function.
As technology advances through innovations like Apple Vision Pro and next-generation VR platforms, the future of 3D vision and movies promises even greater accessibility and enjoyment. Success requires balancing enthusiasm for cutting-edge technology with responsible viewing habits and ongoing awareness of personal visual health needs.
Whether you’re experiencing the magic of 3D vision and movies for the first time or are a longtime enthusiast, staying informed about technological developments and their effects enables optimal choices for both entertainment value and long-term eye health.
For comprehensive eye health evaluations and 3D vision assessments in the Seattle area, consider consulting with specialized optometry practices like Cannon EyeCare, which offers advanced diagnostic technology and personalized care for binocular vision problems and 3D viewing difficulties.
FAQs
-
3D movies use two cameras positioned side by side to capture separate images for each eye. These images are projected simultaneously and combined using polarized glasses to mimic natural stereoscopic vision.