A New Option For Dry Eye Disease Treatment
Dry Eye Disease (DED) impacts millions globally. While numerous treatments exist, most necessitate daily tasks, which make it hard for patients to stick to their regimen. Tixel i (by Novoxel) offers a new, non-invasive option that aims to alleviate both the symptoms and signs of Dry Eye. The majority of patients are likely to have lasting relief from an initial series of 3 treatments; they may not need as many drops and warm compresses after Tixel -i. Studies indicate that eyelid treatments with the the FDA-approved Tixel i can truly enhance a patient’s quality of life.
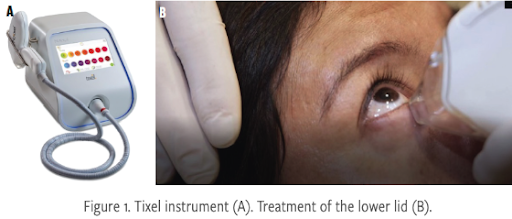
What is Tixel i?
The Tixel treatment is a quick and non-invasive procedure for adults with Dry Eye Disease (DED) who do not have active inflammation or infection. The entire process takes only 2 to 3 minutes and requires no numbing creams or ultrasound gel.
During the treatment, a block of 24 small, blunt titanium pyramids heated to 400*C briefly (and lightly) touch the surface of the skin. The skin is not pierced, and there are no lasers or radiation. Each lid gets ten quick, evenly spaced “pulses” of heat, which melts the meibum (oils) in the Meibomian Glands beneath. As a bonus, treatments over the part of the lid containing the lash follicles can reduce rosacea and demodex mites that contribute to blepharitis and dry eye. Redness and slight skin irritation may occur for up to 4 days post-treatment. In the first 2 days after treatment, makeup, sunscreen, and sun exposure are to be avoided.
Treatment Protocol and Preliminary Results
Treatment Protocol
For optimal results, an initial series of three Tixel treatments is recommended, with each session spaced about 2 weeks apart. For individuals diagnosed with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD), lid scrubbing and meibomian gland expression may be incorporated into the treatment plan. A significant advantage of Tixel treatment is that patients can immediately resume their normal activities upon leaving the clinic, as long as they stay out of the sun for a few days.
Preliminary Results from a Clinical Trial
A significant clinical trial for Tixel treatment at Vallmedic Vision & Aesthetic, Andorra, Europe involved 61 patients diagnosed with Dry Eye Disease (DED).
More than 75% of the enrolled patients successfully completed the 3 initial treatments, plus a few long-term follow-ups. Preliminary findings demonstrate a substantial reduction in DED symptoms. Specifically, the average scores on the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) decreased from 46.0±18.6 to 21.7±13.6. Furthermore, the noninvasive tear breakup time (TBUT) showed an improvement, increasing from 9.4±3.0 seconds to 13.2±2.9 seconds (Figure 3). These compelling results indicate that Tixel eyelid treatment significantly alleviates DED symptoms and effectively addresses the underlying mechanisms of the condition by addressing MGD. (2,3).
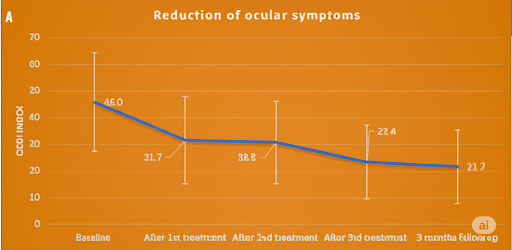
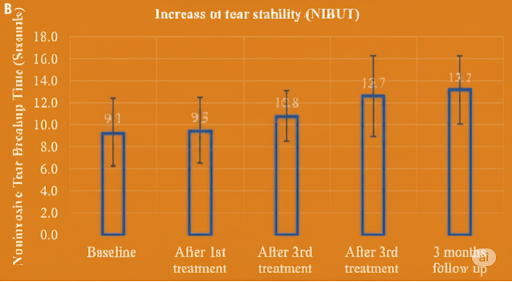
Figure 3. Reduced DED symptoms following TIXEL treatment, as measured by changes in Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) scores (A). Increase in tear film stability after treatment, as indicated by changes in non-invasive tear breakup time (TBUT) (B).
Mechanism of Action
Tixel utilizes a fractional thermomechanical system to deliver treatment by directly conducting heat to the soft tissues of the eyelids. The system comprises a hand piece, connected by a cord to a console, that makes a heated therapeutic titanium tip superficially come into contact with the skin of the eyelid (Figure 4).
The tip, affixed to the distal end of the hand piece, consists of a gold-plated copper base enclosed by a thin-walled titanium alloy cover. The hand piece itself features a precise motion system, driven by a low-inertia linear motor and controlled by a digital signal processor.
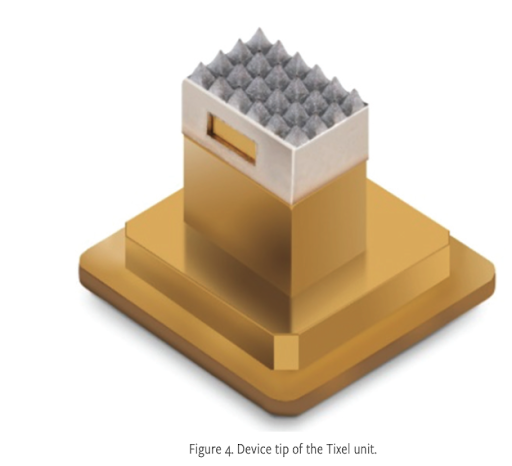
Tip Design and Thermal Mechanism
The Tixel tip, with a surface area of 0.3 cm2, incorporates a 6×4 array of 24 square-based pyramids. Each pyramid is 1.25 mm tall and culminates in a flat, rectangular apex approximately 0.01 mm2 in area. This blunt apex design facilitates efficient heat transfer while preventing mechanical skin puncture.
During treatment, a ceramic heater warms the tip’s base to 400º C (752º F). Skin exposure to the tip is very brief, lasting only 6 milliseconds, which creates a localized, non-ablative, shallow zone of superficial tissue damage. For meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) treatment, the resulting thermal lesion is 200 µm deep and 325 µm wide. In essence a polka-dot pattern of skin in the treatment zone is heated briefly, and the non-treated areas (95% of the surface area) allows for rapid tissue healing.
The heat gets deep enough into the lid to melt any thickened meibum. It also stimulates a robust healing response in the tissues adjacent to the meibomian glands; thus revitalizing the area. The precise pathway by which heat transfer stimulates meibomian gland secretion remains idiopathic and warrants further investigation.
Conclusion
Dry Eye Disease (DED) often receives inadequate attention from eye care professionals, significantly impacting these patient’s long-term quality of life. As a chronic disorder, DED necessitates regular follow-up appointments. Improvement in symptoms through Tixel therapy can encourage patients to adhere to a consistent maintenance schedule with their providers. These patients may need less drops and at-home treatments as a bonus.
Preliminary results regarding Tixel treatment suggest its potential to eliminate or significantly reduce the signs and symptoms of DED in patients unresponsive to conventional modalities like Intense Pulsed Light (IPL). The observed effects of Tixel treatment can persist for 9 to 12 months, positioning it as a potentially indispensable option for the treatment and ongoing management of DED.

Sources
1. Ludger Hanneken,MD,PhD; Sunil Shah, MBBS, FRCOphth, FRCS(Ed), and Debarun Dutta, MCOptom, PhD, FAAO, FHEA, FBCLA. A Novel Option for Treating Dry Eye Disease. Cataract & Refractive Surgery Today, May 2022.
2. Shah S, Hanneken L, Dutta D. Tixel, a completely novel way of treating dry eye. Paper presented at: The 2020 ASCRS Virtual Annual Meeting; May 16, 2020.
3. Shah S, Dutta D, Taneja M, et al. Non-ablative thermomechanical skin treatment for dry eye disease: a prospective multicentre open-label trial. Paper presented at: 39th Congress of the ESCRS; Amsterdam, Netherlands; October 8–11, 2021.
4. Elman M, Fournier N, Barnéon G, Bernstein EF, Lask G. Fractional treatment of aging skin with Tixel, a clinical and histological evaluation. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016;18(1):31-73.
Tixel i Frequently Asked Questions
-
It’s $225 for a ‘routine glasses exam’. An eye exam with a contact lens fitting is a bit more, at about $345 (price varies). Note that the cost is far les with insurance, and many insurance providers cover yearly eye exams fully.
