Eye Dilation Guide for Seattle Eye Exams
If you’re preparing for an eye exam in Seattle and wondering about eye dilation, you’re in the right place. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about pupil dilation during your Seattle eye exam, from the procedure itself to what happens afterward. Whether you’re a busy professional on Capitol Hill or a family in University Village, understanding eye dilation helps you prepare for this essential part of comprehensive eye care.
What Is Eye Dilation and Why Is It Essential for Your Seattle Eye Exam?
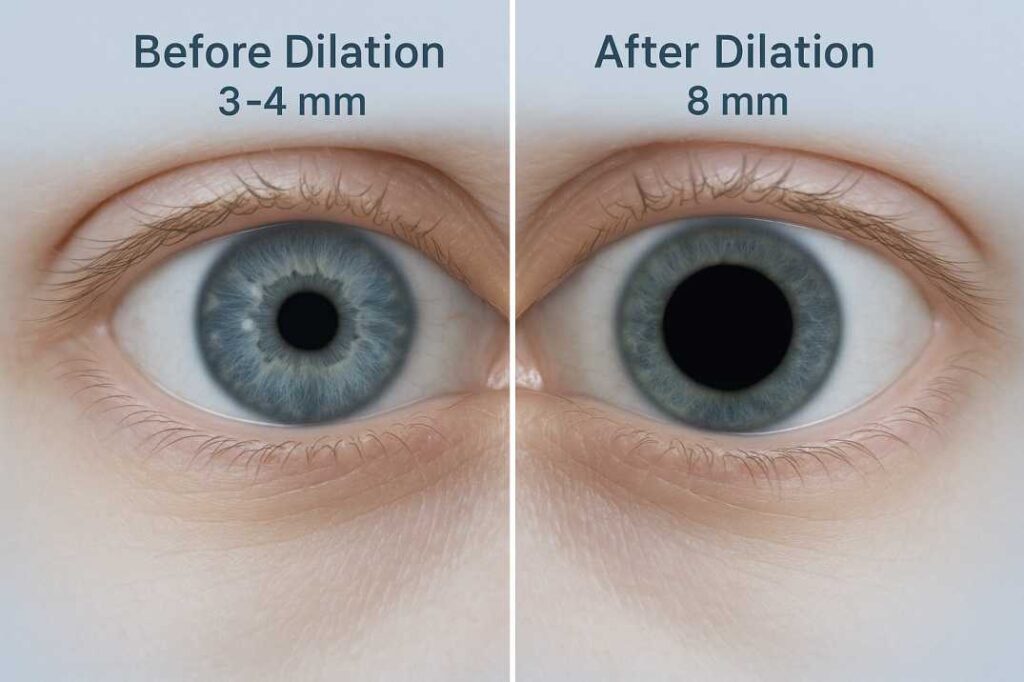
Eye dilation is a routine procedure where your optometrist uses specialized drops to temporarily enlarge your pupils. During dilation, your iris muscles relax, allowing your pupils to widen from their normal 3-4mm to approximately 6-8mm. This creates a larger “window” that enables your eye doctor to examine the internal structures of your eye thoroughly.
Without dilation, your pupils naturally constrict when exposed to bright examination lights, severely limiting your doctor’s view. Non-dilated exams only reveal 10-20% of your retina, potentially missing 85% of disease-prone tissue where serious conditions like glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration often begin.
For Seattle residents, eye dilation is particularly important due to specific regional risk factors. The Pacific Northwest’s unique environmental conditions, combined with our tech-heavy workforce spending long hours on digital devices, create an increased risk for certain eye conditions that require comprehensive screening through dilated examinations.
The Science Behind Eye Dilation
During dilation, your optometrist typically applies two types of eye drops. The first contains a muscarinic receptor antagonist (usually 1% tropicamide) that paralyzes the muscle controlling pupil constriction. The second often contains 2.5% phenylephrine, an alpha-receptor agonist that stimulates the muscle responsible for pupil widening.
Recent research published in the Journal of Optometric Education demonstrates that 94.5% of optometrists are comfortable using tropicamide, while some exercise more caution with phenylephrine due to its cardiovascular effects. This dual-drop approach ensures maximum pupil dilation in shorter timeframes, even for patients with dark-colored irises or age-related changes that resist single-agent dilation.
How Long Does Eye Dilation Take and Last?
The Dilation Timeline
The complete dilation process follows a predictable timeline:
Initial Application (0-5 minutes): Your optometrist applies the dilating drops to both eyes. You may experience brief stinging or discomfort, which is completely normal.
Waiting Period (20-30 minutes): Your pupils gradually enlarge as the medication takes effect. During this time, you’ll begin noticing increased light sensitivity.
Examination Phase (10-15 minutes): Once fully dilated, your doctor performs a comprehensive examination of your retina, optic nerve, and other internal eye structures.
Recovery Period (3-6 hours): The effects gradually wear off as your body metabolizes the medication.
Factors Affecting Dilation Duration
Several factors influence how long dilation lasts:
Eye Color: People with lighter-colored eyes (blue, green, hazel) typically experience longer-lasting effects than those with brown eyes. The increased pigmentation in darker irises helps metabolize the medication more quickly.
Age: Children and young adults often experience longer dilation periods due to stronger iris muscles requiring more potent drops.
Individual Metabolism: Your body’s rate of processing the medication varies based on overall health, medications, and genetic factors.
Drop Strength: Stronger concentrations used for patients with resistant pupils may extend the duration.
What to Expect During Your Dilated Eye Exam in Seattle
Before Your Appointment
To ensure a smooth experience at your Seattle eye care provider:
Arrange Transportation: Plan for someone to drive you home, especially if this is your first dilation experience. While many patients can drive safely after dilation, first-time patients should err on the side of caution.
Bring Sunglasses: Seattle’s frequent overcast skies help, but sunglasses remain essential for post-exam comfort.
Schedule Wisely: Avoid scheduling important computer work or detailed reading immediately after your appointment.
Medical History: Inform your doctor about any medications, allergies, or previous adverse reactions to eye drops.
During the Examination
Your Seattle optometrist will use advanced diagnostic equipment to examine:
The Retina: Checking for early signs of diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and retinal tears or detachments.
Optic Nerve: Assessing for glaucoma damage, which is particularly important given Seattle’s aging professional population.
Blood Vessels: Looking for signs of hypertension, diabetes, and other systemic conditions that manifest in the eye.
Vitreous: Examining the gel-like substance filling your eye for floaters, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
Side Effects and What to Avoid After Eye Dilation
Common Side Effects
Understanding what’s normal helps you prepare and stay comfortable:
Blurred Near Vision: The drops temporarily paralyze your focusing muscles, making it difficult to read or see objects up close. This affects everyone differently, but typically makes reading nearly impossible for several hours.
Light Sensitivity: Your enlarged pupils allow significantly more light to enter your eyes, making even normal indoor lighting uncomfortable. Outdoor light can be particularly bothersome.
Difficulty Focusing: Your eyes cannot adjust focus normally, making tasks requiring visual precision challenging.
Activities to Avoid
For your safety and comfort, avoid these activities until the effects wear off:
Driving: While not legally prohibited, driving with dilated pupils poses safety risks due to increased glare sensitivity and reduced ability to quickly adjust to changing light conditions.
Computer Work: Extended screen time can cause significant discomfort and eye strain. If you must use devices, reduce brightness and take frequent breaks.
Reading: Close-up tasks requiring fine detail work become extremely difficult and may cause headaches.
Bright Outdoor Activities: Direct sunlight can be painful and may cause temporary vision problems.
Managing Discomfort
To minimize post-dilation discomfort:
- Wear wraparound sunglasses that block light from all angles
- Stay in dimly lit environments when possible
- Use artificial tears if your eyes feel dry
- Avoid rubbing your eyes, which may prolong irritation
Dilation vs. Alternative Technologies: Making the Right Choice for Your Seattle Eye Exam
Traditional Dilation: The Gold Standard
Traditional dilation remains the most comprehensive method for examining internal eye structures. It provides:
- 100% retinal visibility for complete assessment
- Ability to detect subtle changes in early disease stages
- Cost-effective inclusion in routine eye exams
- Proven track record over decades of use
Optomap Technology: The Modern Alternative
Many Seattle eye care providers now offer Optomap retinal imaging as an alternative or supplement to dilation. This technology:
- Captures 82% of the retina in seconds without drops
- Creates permanent digital records for comparison
- Eliminates post-exam side effects
- Costs an additional $30-40 at most practices
When to Choose Each Option
Choose Traditional Dilation For:
- Comprehensive annual exams
- History of eye disease or family risk factors
- Diabetes or hypertension monitoring
- New patient examinations
- Any concerning symptoms
Consider Optomap For:
- Routine follow-up appointments
- Patients who cannot tolerate the dilation side effects
- Time-sensitive situations requiring immediate return to work
- Patients with transportation limitations
Your Seattle optometrist may recommend combining both technologies for optimal care, particularly for high-risk patients.
Who Should Avoid Eye Dilation?
While eye dilation is safe for most people, certain conditions require special consideration:
Medical Contraindications
Narrow-Angle Glaucoma: Patients with narrow anterior chamber angles may experience acute angle-closure glaucoma following dilation. Your optometrist will assess your anterior chamber depth before proceeding.
Severe Cardiovascular Disease: The cardiovascular effects of phenylephrine may concern doctors treating patients with unstable heart conditions or uncontrolled hypertension.
Recent Eye Surgery: Patients recovering from certain eye surgeries may need to postpone dilation until healing is complete.
Pregnancy Considerations
Current research indicates that eye dilation during pregnancy is generally safe, but many practitioners prefer conservative approaches. Discuss the risks and benefits with your optometrist, particularly during the first trimester.
Age-Related Considerations
Children: Pediatric dilation often requires stronger drops and may last longer. Parent or guardian presence is typically required.
Elderly Patients: Older adults may experience extended dilation periods and increased fall risk due to visual impairment.
Seattle-Specific Eye Health Considerations
Environmental Risk Factors
Seattle’s unique environment creates specific eye health challenges:
UV Exposure: Despite frequent cloud cover, UV rays penetrate clouds and reflect off water and snow. This increases risk for cataracts and macular degeneration.
Screen Time: Our tech-heavy economy means many Seattle residents spend 8+ hours daily on digital devices, increasing dry eye and computer vision syndrome risks.
Air Quality: Seasonal smoke from wildfires can exacerbate dry eye conditions and allergic reactions.
Vitamin D Deficiency: Limited sunlight exposure may affect overall eye health and increase myopia progression.
Regional Health Trends
Seattle’s population faces increased risks for:
Diabetes: Growing rates of type 2 diabetes necessitate regular diabetic retinopathy screening through dilated exams.
High Blood Pressure: Stress from urban living and sedentary tech jobs contributes to hypertension, which manifests in retinal blood vessel changes visible only through dilation.
Age-Related Conditions: Our aging professional population needs proactive screening for glaucoma and macular degeneration.
Recent Research on Eye Dilation Safety and Effectiveness
2024 Safety Studies
Recent research published in PMC journals examined the safety profile of routine pupil dilation in clinical settings. The studies found that adverse events remain extremely rare, occurring in less than 0.1% of procedures. However, researchers emphasized the importance of proper patient screening and post-procedure monitoring.
Cardiovascular Safety Research
A 2024 study in the Journal of Optometric Education investigated optometrists’ practices regarding blood pressure thresholds for dilation. The research found that 45.2% of practitioners avoid dilating patients with systolic pressure above 200mmHg, while 34.3% use a diastolic threshold of 105mmHg. These conservative approaches reflect medical-legal concerns rather than evidence-based contraindications.
Biometric Impact Studies
Recent research using advanced optical coherence tomography examined how dilation affects various eye measurements. The studies found statistically significant but clinically minor changes in corneal thickness, anterior chamber depth, and lens positioning. These findings confirm that dilation doesn’t substantially impact the accuracy of routine eye measurements.
Preparing for Your Seattle Eye Dilation: A Step-by-Step Guide
One Week Before
- Review your current medications with your optometrist
- Schedule time off work for the afternoon if possible
- Arrange backup transportation options
Day of Your Appointment
- Bring current eyeglasses and contact lens information
- Arrive with sunglasses
- Eat normally (dilation doesn’t require fasting)
- Remove contact lenses before arrival unless specifically instructed otherwise.e
What to Bring
- Current prescription glasses
- Sunglasses (wraparound style preferred)
- Insurance cards and identification
- List of current medications
- Transportation arrangements confirmation
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Eye Dilation in Seattle
Typical Costs
Eye dilation is usually included in the cost of comprehensive eye examinations, which range from $150-$300 in the Seattle area, depending on the provider and complexity of testing.
Insurance Coverage
Most vision and medical insurance plans cover routine dilated eye exams:
Vision Insurance: VSP, EyeMed, and other vision plans typically cover annual dilated exams with minimal copays.
Medical Insurance: Medicare, Premera, Regence, and Kaiser cover medically necessary dilated exams, particularly for diabetic patients and those with glaucoma risk factors.
HSA/FSA Eligibility: Dilated eye exams qualify for health savings account and flexible spending account reimbursement.
Additional Testing Costs
Advanced imaging like Optomap typically costs extra ($30-40) and may not be covered by insurance unless medically necessary.
When to Schedule Your Next Dilated Eye Exam
Recommended Frequencies
Ages 18-39: Every 2-4 years for healthy individuals, annually if you have risk factors
Ages 40-54: Every 2-3 years, or annually with a family history of eye disease
Ages 55-64: Every 1-2 years, as age-related conditions become more common
Ages 65+: Annually due to increased risk for glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic complications
Risk Factors Requiring More Frequent Exams
- Diabetes (any type)
- Family history of glaucoma or macular degeneration
- High myopia (nearsightedness)
- Previous eye injuries or surgeries
- Hypertension or cardiovascular disease
- African American or Hispanic ethnicity (higher glaucoma risk)
Finding the Right Seattle Eye Care Provider for Dilation
What to Look For
Board Certification: Ensure your optometrist or ophthalmologist maintains current professional credentials.
Modern Equipment: Look for practices with advanced diagnostic technology and imaging capabilities.
Experience with Dilation: Choose providers comfortable with both traditional dilation and alternative technologies.
Emergency Protocols: Verify the practice has procedures for handling rare adverse reactions.
Questions to Ask
- How often do you recommend dilated exams for someone with my risk factors?
- Do you offer Optomap or other dilation alternatives?
- What should I do if I experience prolonged dilation effects?
- How do you handle patients with narrow angles or other risk factors?
Emergency Situations: When to Seek Immediate Care
While serious complications from eye dilation are extremely rare, seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Severe Eye Pain: Particularly if accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or headache (possible angle-closure glaucoma)
Sudden Vision Loss: Any significant decrease in vision beyond expected dilation effects
Persistent Nausea/Vomiting: May indicate increased eye pressure or an adverse drug reaction
Chest Pain or Rapid Heartbeat: Possible cardiovascular reaction to phenylephrine
Allergic Reactions: Hives, facial swelling, or difficulty breathing require emergency treatment
The Future of Eye Dilation and Examination Technology
Emerging Technologies
Research continues into dilation-free examination methods:
Adaptive Optics: Advanced imaging systems that may eliminate the need for dilation in some cases
AI-Enhanced Imaging: Artificial intelligence helping detect diseases from non-dilated retinal photographs
Improved Medications: Development of shorter-acting dilating agents for reduced side effects
What This Means for Seattle Patients
As technology advances, Seattle eye care providers will likely offer more options for comprehensive eye examinations. However, traditional dilation will remain the gold standard for thorough eye health assessment for the foreseeable future.
Key Resources and Research Citations
This comprehensive guide draws from current medical research and professional standards to provide Seattle residents with accurate, evidence-based information about eye dilation. Here are three key resources that informed this article:
1. Journal of Optometric Education – Blood Pressure and Dilation Practices
“Teaching Pupil Dilation: Faculty Perceptions Regarding Elevated Blood Pressure and Dilating Agents” (2018)
This peer-reviewed study surveyed 73 optometry faculty members about their practices regarding pupil dilation in patients with elevated blood pressure. The research found that 94.5% of optometrists were comfortable using 1% tropicamide, while 64.4% expressed concerns about 2.5% phenylephrine. The study revealed that 45.2% of practitioners avoid dilating patients with systolic pressure above 200mmHg, providing important safety guidelines referenced throughout our article.
2. PMC (PubMed Central) – Safety Guidelines for Research Dilation
“Pupillary Dilation in Research: More than Meets the Eye” (2022)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9276640/
This comprehensive review, published in PMC, examined safety protocols for pupil dilation in research settings, with findings applicable to clinical practice. The study emphasized the importance of pre-dilation screening for narrow angles, medical contraindications, and proper informed consent. This research informed our sections on who should avoid dilation and emergency protocols, contributing to the safety information provided to Seattle patients.
3. American Academy of Ophthalmology – Patient Education Resources
“What to Expect When Your Eyes Are Dilated” (2019, updated 2024)
https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/dilating-eyedrops
The AAO’s official patient education resource provides evidence-based information about dilation duration, side effects, and recovery guidelines. This authoritative source confirmed our 3-6 hour duration estimates and helped establish the timeline information provided throughout the article. The AAO’s guidelines also supported our recommendations for post-dilation care and activity restrictions.
Additional supporting research from optometry journals, medical databases, and professional organizations was consulted to ensure accuracy and completeness of all information presented.
Key Takeaways for Seattle Eye Exam Patients
Eye dilation remains an essential component of comprehensive eye care, providing unparalleled visibility into your eye health. While the temporary side effects can be inconvenient, the diagnostic benefits of eye dilation far outweigh the discomfort for most patients.
Seattle residents should expect dilation during routine comprehensive eye exams, particularly given our region’s specific risk factors. The procedure is safe, effective, and provides crucial information about your overall health beyond just your vision.
By understanding what to expect and properly preparing for dilation, you can ensure a comfortable experience while receiving the thorough eye care you need to maintain healthy vision for years to come.
Ready to schedule your comprehensive dilated eye exam? Contact your Seattle eye care provider to discuss whether traditional dilation, alternative imaging, or a combination approach is right for your individual needs and lifestyle.
For personalized eye care delivered with the thoroughness and attention you deserve, consider Cannon EyeCare, conveniently located in University Village and Pike Place Market. Our experienced medical team combines clinical expertise with genuine Midwestern hospitality, ensuring you receive comprehensive eye examinations in a comfortable, unhurried environment. Our comprehensive services include contact lens fittings, advanced dry eye treatment protocols, and specialized diabetic eye care management. Contact us today to schedule your appointment and discover the difference that truly personalized, patient-centered care makes in your eye health journey.
Medical Disclaimer: This publication provides general medical information about eye dilation procedures and should not substitute for professional medical consultation. Individual patient experiences may vary significantly. Always consult with your licensed optometrist or ophthalmologist regarding your specific medical condition, treatment options, and care needs. The information presented reflects current medical standards as of September 2025.