Retinal Photography: What It Shows and Why It Matters
Your Complete Guide to Advanced Eye Care Technology
Executive Summary: Retinal photography represents a revolutionary advancement in preventive eye care, providing non-invasive visualization of your ocular and systemic health. This comprehensive diagnostic technology can detect serious conditions—including diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and macular degeneration—years before symptoms manifest, making it an indispensable tool for early intervention and vision preservation.
Understanding Retinal Photography: The Foundation of Modern Eye Care
Retinal photography—also termed retina imaging or digital retinal imaging—represents a paradigm shift in ocular examination methodology. This sophisticated diagnostic modality captures high-resolution digital images of the retina, optic nerve, retinal vasculature, and macula, providing clinicians with detailed anatomical insights that traditional examination techniques cannot achieve.
What is retinal photography? Fundamentally, retinal photography creates a comprehensive topographical map of one of the human body’s most intricate and metabolically active tissues. The retina serves as the neural interface where photons are converted to electrical signals, while the optic disc houses the optic nerve fibers that transmit visual information to the brain. Unlike the limited field of view afforded by conventional direct ophthalmoscopy, retinal photography provides extensive documentation that enables longitudinal monitoring of subtle pathological changes.
The Technology Behind Retinal Photography
Contemporary retinal photography systems employ advanced digital imaging arrays and precisely calibrated illumination systems to capture detailed anatomical images through the pupillary aperture. These systems utilize low-power laser diodes or LED arrays to generate optimal contrast while minimizing patient discomfort and ensuring safety across all demographic populations.
The imaging process is characterized by its efficiency and patient comfort. During examination, patients simply maintain visual fixation on a target stimulus while the imaging system captures multiple high-resolution frames in milliseconds. This rapid acquisition minimizes motion artifacts while providing comprehensive documentation of retinal anatomy.
What Does Retinal Photography Show? A Window to Systemic Health
Ocular Pathologies Detected Through Retinal Photography
What conditions can retinal photography detect? Retinal photography demonstrates exceptional diagnostic capability across a broad spectrum of ocular pathologies, frequently identifying disease processes during their subclinical phases when therapeutic intervention yields optimal outcomes:
Diabetic Retinopathy: Chronic hyperglycemia induces characteristic microvascular changes within the retinal vasculature, including microaneurysm formation, intraretinal hemorrhages, and neovascularization. Retinal photography enables detection of these pathognomonic changes before visual symptoms manifest, facilitating early therapeutic intervention to prevent irreversible vision loss.
Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy: This progressive neurodegenerative condition causes characteristic excavation of the optic nerve head and retinal nerve fiber layer thinning. Advanced retinal photography systems can quantify these structural changes with micrometer precision, enabling early detection and monitoring of disease progression.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): This leading cause of central vision loss in developed nations manifests through drusen accumulation, retinal pigment epithelium changes, and, in advanced cases, choroidal neovascularization. Retinal photography provides high-resolution documentation of these pathological changes, enabling prompt referral for specialized treatment.
Retinal Detachment: Separation of the neurosensory retina from the underlying retinal pigment epithelium represents an ophthalmologic emergency. Retinal photography can identify subtle signs of impending detachment, including retinal tears and localized detachments, facilitating emergent intervention.
Ocular Melanoma: Primary intraocular malignancies may present as pigmented lesions within the retina or choroid. Early identification through retinal photography enables prompt oncologic evaluation and treatment before metastatic spread occurs.
Systemic Health Assessment Through Retinal Vascular Analysis
The retinal vasculature provides the unique opportunity for direct, non-invasive visualization of the human microcirculatory system. This distinctive anatomical access enables retinal photography to serve as a diagnostic window into systemic vascular health, often revealing pathological changes before clinical symptoms manifest elsewhere.
Hypertensive Retinopathy: Systemic hypertension produces characteristic retinal vascular changes, including arteriovenous nicking, copper wire arterial changes, and flame-shaped hemorrhages. These findings often precede other clinical manifestations of hypertensive end-organ damage.
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment: Emerging research demonstrates strong correlations between retinal microvascular abnormalities and cardiovascular morbidity. Specific vascular caliber measurements and tortuosity indices serve as predictive biomarkers for future cardiac events.
Neurological Disorders: The retina’s embryologic origin as an extension of the central nervous system enables detection of neurodegenerative processes. Current research investigates retinal biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, with promising preliminary results.
Clinical Modalities in Retinal Photography: Optimizing Diagnostic Approach
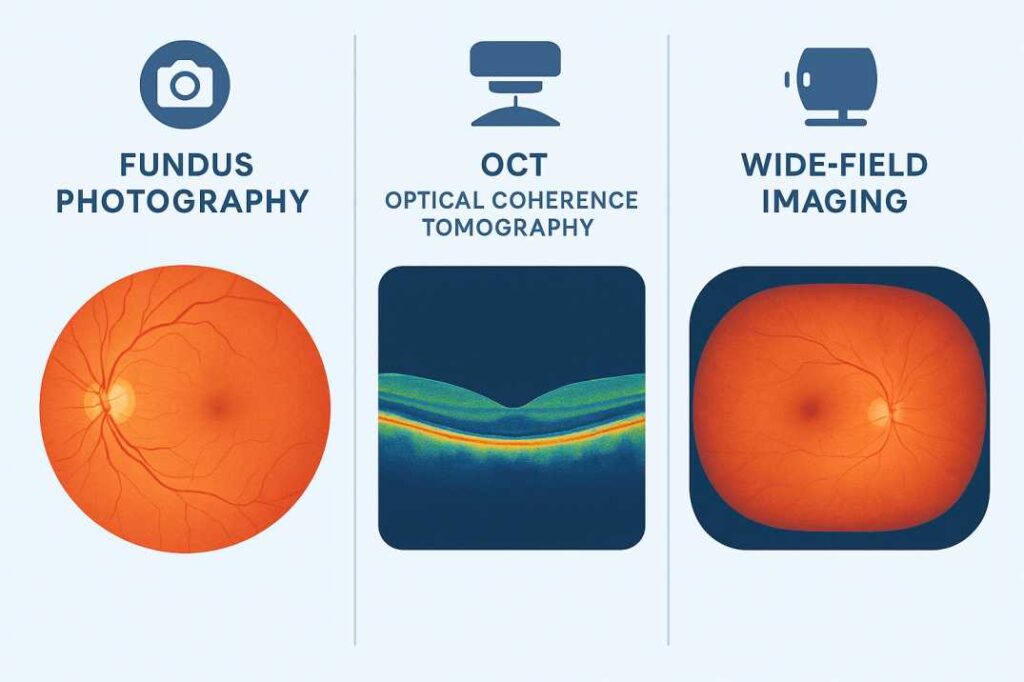
Fundus Photography
Conventional fundus photography remains the cornerstone of retinal documentation. This established modality employs specialized camera systems to capture detailed color images of the posterior segment, providing excellent visualization of retinal surface anatomy and pathology.
Clinical Advantages:
- Rapid image acquisition with minimal patient discomfort
- Superior documentation of surface retinal pathology
- Established baseline for longitudinal comparison studies
- Minimal preparation requirements and broad applicability
Technical Limitations:
- Limited depth resolution for subsurface pathology
- Reduced sensitivity for early intraretinal changes
- Dependence on media clarity for optimal image quality
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography represents the current gold standard for high-resolution retinal imaging. This technology employs near-infrared light interferometry to generate cross-sectional images of retinal architecture with axial resolution approaching cellular dimensions.
Clinical Applications:
- Quantitative assessment of retinal layer thickness with micrometer precision
- Detection of subclinical macular edema and intraretinal fluid
- Monitoring of therapeutic response in retinal diseases
- Early identification of glaucomatous nerve fiber layer loss
Advanced OCT Modalities:
- OCT Angiography (OCTA) for non-invasive vascular imaging
- Enhanced depth imaging for choroidal assessment
- Swept-source technology for improved penetration through media opacities
Ultra-Widefield Retinal Imaging
Contemporary ultra-widefield imaging systems provide unprecedented visualization of the peripheral retina, capturing up to 200 degrees of retinal anatomy in a single acquisition. This technology addresses the historical limitation of conventional fundus photography’s restricted field of view.
Clinical Significance:
- Enhanced detection of peripheral retinal pathology
- Comprehensive documentation for surgical planning
- Improved monitoring of diabetic retinopathy progression
- Superior visualization of retinal vascular abnormalities
The Optos ultra-widefield platform exemplifies this technology’s clinical utility, enabling detection of pathology that traditional imaging modalities might overlook, particularly in the retinal periphery, where many sight-threatening conditions initially manifest.
Patient Safety and Procedural Considerations
Safety Profile and Risk Assessment
Is retinal photography safe? Retinal photography demonstrates an exceptional safety profile across all patient demographics. The procedure utilizes low-intensity illumination sources that comply with established ocular safety standards, ensuring no risk of phototoxic retinal damage.
Safety Characteristics:
- Non-contact methodology eliminates infection transmission risk.
- Low-intensity light exposure well below established safety thresholds
- Absence of ionizing radiation or contrast agents in standard imaging
- Immediate resumption of normal activities post-procedure
- Suitability for pediatric, geriatric, and pregnant populations
Clinical Procedure and Patient Experience
What happens during retinal photography? The imaging procedure is designed for optimal patient comfort while maintaining diagnostic quality. Patients are positioned at the imaging device with appropriate head stabilization to minimize motion artifacts during image acquisition.
Procedural Sequence:
- Patient positioning with chin rest and forehead stabilization
- Visual fixation on the designated target stimulus
- Automated focus adjustment and exposure optimization
- Rapid image acquisition (typically <1 second per eye)
- Immediate image review and quality assessment
- Additional imaging if clinically indicated
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Standard retinal photography requires minimal patient preparation, contributing to its utility as a screening modality:
- No fasting or medication restrictions required
- Contact lens removal if present
- Pupillary dilation may be indicated for comprehensive imaging
- Transportation arrangements if mydriatic agents are employed
Post-Procedure Considerations
Most retinal photography procedures enable immediate return to normal activities. However, when pharmacologic pupillary dilation is employed, patients may experience temporary photophobia and reduced accommodation for 2-6 hours post-procedure, necessitating transportation arrangements and sun protection.
Advanced Applications: The Future of Retinal Photography
Artificial Intelligence Integration in Clinical Practice
The integration of artificial intelligence represents a transformative development in retinal image analysis. Recent 2025 research from the National Institutes of Health demonstrates that AI-enhanced systems achieve 100-fold improvements in imaging speed while simultaneously improving image contrast by 3.5-fold.
Current AI Applications in Clinical Practice:
- Automated diabetic retinopathy screening with 92-96% diagnostic accuracy
- Real-time detection of age-related macular degeneration biomarkers
- Quantitative assessment of retinal vascular parameters
- Predictive modeling for disease progression risk stratification
Breakthrough 2025 Technologies:
- Parallel discriminator generative adversarial networks (P-GAN) for enhanced image processing
- Adaptive optics integration reduces acquisition time by two orders of magnitude
- Cellular-level retinal pigment epithelium imaging using standard clinical instrumentation
- FDA-approved autonomous AI systems for point-of-care diabetic retinopathy screening
Genetic Risk Assessment
Cutting-edge research is combining retinal photography with genetic analysis to predict future health risks. Researchers found significant associations between the thinning of different retinal layers and increased risk of developing ocular, cardiac, pulmonary, metabolic, and neuropsychiatric diseases.
This emerging field promises to transform retinal photography from a diagnostic tool into a predictive health assessment platform.
Telemedicine Applications
Portable retinal photography systems are expanding access to eye care, particularly in underserved areas. Portable fundus photography can shift diabetic retinopathy screening into primary care offices, community clinics, and home healthcare settings.
Making Informed Decisions: Cost, Insurance, and Value
Understanding the Investment
The cost of retinal photography varies by provider and technology type. Most eye care practices charge between $30 – $60 for retinal imaging, with many practices charging around $39-$49 for this service. Some providers may include it in the total cost of an eye exam.
Insurance Coverage Considerations
Insurance coverage for retinal photography is complex and varies significantly by plan type and intended use. Vision insurance plans generally do not cover retinal photography when used for routine screening, as it’s considered “healthy eye imaging.” However, medical insurance may cover retinal photography when there’s a documented medical necessity, such as monitoring existing conditions like diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Coverage typically depends on:
- Whether it’s used for routine screening vs. medical monitoring
- Your specific insurance plan terms
- The medical necessity documented by your provider
- Whether you’re seeing an ophthalmologist vs. an optometrist
Some federal vision plans have reduced copays for retinal imaging – for example, BCBS FEP Vision reduced its retinal imaging copay from $39 to $29 in 2025. It’s important to check with your specific insurance provider about coverage before your appointment.
Value-Based Healthcare Assessment
When evaluating the clinical utility of retinal photography, healthcare economists increasingly recognize its role in preventive medicine and early disease detection. The technology’s capacity to identify pathological processes during subclinical phases can substantially reduce long-term healthcare costs by enabling timely therapeutic intervention before irreversible complications develop.
Economic Considerations for Patient Decision-Making:
- Personal and familial ocular disease risk profiles
- Systemic health conditions requiring ocular monitoring
- Long-term healthcare cost implications of delayed diagnosis
- Quality of life preservation through vision maintenance
Clinical Applications Across Patient Demographics
Pediatric and Adolescent Populations
Is retinal photography safe for children and pregnant women? Retinal photography demonstrates excellent safety and tolerability across all age groups, utilizing low-intensity illumination that poses no risk of ocular damage. Pediatric applications offer unique advantages in clinical practice:
- Elimination of pharmacologic mydriasis reduces patient anxiety and parental concerns
- Rapid image acquisition minimizes cooperation requirements
- Longitudinal documentation enables monitoring of developmental changes
- Early detection of inherited retinal dystrophies and amblyogenic factors
Adult Diabetic Populations
For patients with diabetes mellitus, retinal photography represents an essential component of comprehensive diabetes management. The American Diabetes Association recommends annual dilated eye examinations for diabetic patients, with retinal photography serving as both a screening and monitoring modality.
Clinical Benefits in Diabetic Care:
- Detection of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy before symptomatic presentation
- Quantitative monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic response
- Risk stratification for proliferative disease development
- Integration with systemic diabetes management protocols
Geriatric Patient Considerations
The aging population faces increased susceptibility to multiple ocular pathologies, making retinal photography particularly valuable for comprehensive geriatric eye care. Age-related changes in ocular media clarity may necessitate specialized imaging protocols to optimize diagnostic quality.
Age-Related Clinical Applications:
- Age-related macular degeneration monitoring and staging
- Glaucomatous progression assessment in elderly populations
- Hypertensive retinopathy evaluation as a cardiovascular risk marker
- Medication-related retinal toxicity screening (particularly hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine)
Clinical Integration and Comparative Analysis
Retinal Photography Versus Traditional Diagnostic Modalities
What’s the difference between retinal photography and eye dilation? While both modalities serve essential roles in comprehensive ocular examination, they offer complementary rather than competing capabilities. Retinal photography provides superior documentation and longitudinal comparison capabilities, while pharmacologic mydriasis enables comprehensive peripheral retinal assessment.
Comparative Advantages of Retinal Photography:
- Elimination of post-procedure visual impairment and photophobia
- Immediate return to normal activities, including driving and close work
- Permanent digital documentation for longitudinal analysis
- Enhanced patient acceptance and procedural compliance
- Objective image analysis capabilities with reduced inter-examiner variability
Clinical Integration Strategies: Contemporary practice standards increasingly incorporate both modalities in a complementary fashion, utilizing retinal photography for routine documentation and monitoring while reserving pharmacologic mydriasis for comprehensive peripheral examination when clinically indicated.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques and Multimodal Imaging
For complex cases requiring enhanced diagnostic precision, specialized retinal photography techniques may be employed:
Fluorescein Angiography: This contrast-enhanced imaging modality enables dynamic assessment of retinal circulation through intravenous fluorescein administration. While generally well-tolerated, patients may experience temporary skin discoloration or urine pigmentation lasting 24-48 hours. Rare allergic reactions necessitate appropriate medical supervision during the procedure.
Clinical Applications of Fluorescein Angiography:
- Assessment of retinal vascular perfusion patterns
- Detection of occult choroidal neovascularization
- Evaluation of blood-retinal barrier integrity
- Monitoring of anti-VEGF therapeutic response in neovascular conditions
Optimizing Patient Outcomes Through Strategic Implementation
Establishing Baseline Documentation and Longitudinal Monitoring
The clinical value of retinal photography increases exponentially when implemented as part of a systematic longitudinal monitoring program. Baseline documentation during periods of ocular health provides essential reference points for detecting subtle pathological changes during subsequent examinations.
Optimal Implementation Strategies:
- Annual baseline imaging for all patients over age 40
- Increased frequency monitoring for high-risk populations
- Standardized imaging protocols ensure consistency across examinations
- Comprehensive digital archival systems enabling long-term comparison studies
Patient Education and Shared Decision-Making
Effective patient education enhances the clinical value of retinal photography by promoting informed participation in healthcare decisions. Patients benefit from understanding the technology’s capabilities, limitations, and role within comprehensive eye care.
Educational Priorities:
- Explanation of retinal anatomy and function in systemic health
- Discussion of individual risk factors and screening recommendations
- Review of imaging findings and their clinical significance
- Establishment of appropriate follow-up protocols based on findings
Lifestyle Factors That Impact Results
Several lifestyle factors can influence retinal health and imaging quality:
- Blood sugar control for diabetic patients
- Blood pressure management
- Smoking cessation
- UV protection through quality sunglasses
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet
Recent Scientific Breakthroughs and Future Directions
Contemporary Scientific Literature
Recent peer-reviewed research continues to expand our understanding of retinal photography’s clinical applications and diagnostic capabilities. The 2024 landmark study published in Science Translational Medicine by Mass Eye and Ear researchers represents a pivotal advancement in our understanding of the retina’s predictive capacity for systemic health assessment.
Key Research Findings:
- Analysis of 44,823 UK Biobank participants revealed significant associations between retinal layer architecture and future disease risk
- Identification of specific retinal biomarkers predictive of cardiovascular, neurological, and metabolic pathology
- Establishment of genetic correlations between retinal morphology and systemic disease susceptibility
- Validation of retinal imaging as a tool for personalized risk assessment
Technological Innovation in 2025
The National Eye Institute’s recent breakthrough in AI-enhanced adaptive optics represents a paradigm shift in retinal imaging capabilities. This technology demonstrates 100-fold improvements in acquisition speed while achieving 3.5-fold enhancements in image contrast, making cellular-level retinal visualization accessible to standard clinical practice.
Clinical Implications:
- Enhanced diagnostic sensitivity for subclinical pathology
- Reduced patient examination times while improving diagnostic yield
- Integration of advanced imaging capabilities into routine clinical workflows
- Potential for earlier therapeutic intervention based on improved diagnostic precision
Regulatory Developments and Clinical Validation
The FDA’s approval of the AEYE-DS algorithm in 2024 represents a milestone in autonomous diagnostic AI systems. This fully automated platform achieves 92-93% sensitivity and 89-94% specificity for diabetic retinopathy detection using handheld imaging devices, validating the clinical utility of AI-assisted diagnosis in decentralized healthcare settings.
Additionally, the regulatory approval of multiple smartphone-based retinal imaging systems, including the Remidio FOP NM-10 and Welch Allyn i-Examiner, demonstrates the feasibility of expanding retinal screening to previously underserved populations through mobile health initiatives.
Advanced Imaging Modalities
Future developments in retinal photography include:
- Adaptive optics for cellular-level resolution
- Fluorescence lifetime imaging for metabolic assessment
- Multi-spectral imaging for enhanced tissue characterization
- Real-time vessel flow analysis
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Safety and Comfort
One of the most common patient concerns involves safety and comfort. Retinal imaging is considered completely safe, with minimal side effects that usually pass within a few minutes.
The procedure involves:
- No physical contact with your eyes
- Low-intensity light that’s safe for all ages
- No lasting effects or complications
- Immediate return to normal activities
Accuracy and Reliability
Modern retinal photography systems demonstrate exceptional accuracy. Retinal photography has high sensitivity, specificity, and inter-/intra-examination agreement compared to in-person ophthalmologist examination.
These systems consistently detect:
- Early-stage disease markers
- Subtle changes over time
- Multiple conditions simultaneously
- Risk factors before symptoms develop
Technology Limitations
While retinal photography is highly advanced, understanding its limitations helps set appropriate expectations:
- Some peripheral retinal areas may require additional imaging
- Certain conditions benefit from complementary testing
- Image quality can be affected by media opacities
- Interpretation requires skilled professionals
Making Retinal Photography Work for You
Personalized Risk Assessment
Your eye care provider can help determine the most appropriate retinal photography approach based on:
- Personal health history
- Family history of eye disease
- Current medications and conditions
- Lifestyle and occupational factors
- Previous eye examination findings
How Often Should You Get Retinal Photography?
How often should you get retinal photography? It’s recommended to get retinal photography every year during your routine eye exam to monitor eye health and track changes over time.
However, frequency may vary based on:
- Age and risk factors
- Existing eye conditions
- Response to previous treatments
- Provider recommendations
- Insurance coverage patterns
Clinical Significance and Future Healthcare Integration
The Role of Retinal Photography in Preventive Medicine
Retinal photography represents a paradigmatic example of preventive medicine’s evolution toward early detection and intervention strategies. Why is retinal photography important? The technology’s capacity to identify pathological processes during subclinical phases enables therapeutic intervention before irreversible tissue damage occurs, fundamentally altering disease prognosis and visual outcomes.
The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced imaging modalities continues to enhance diagnostic capabilities, with emerging applications extending beyond traditional ophthalmology into systemic health assessment and personalized medicine applications.
Future Directions in Retinal Health Assessment
As research continues to elucidate the relationships between retinal morphology and systemic health, retinal photography will likely assume an increasingly central role in comprehensive healthcare delivery. The convergence of imaging technology, artificial intelligence, and genomic medicine promises to transform retinal assessment from a diagnostic procedure into a comprehensive health risk stratification platform.
Whether implemented for routine screening, disease monitoring, or research applications, retinal photography offers an unparalleled combination of safety, diagnostic capability, and clinical utility that positions it as an essential component of contemporary healthcare delivery.
Clinical Excellence in Seattle: Cannon EyeCare
Advanced Retinal Photography Services
Cannon EyeCare, strategically located in Seattle’s University Village and Pike Place Market districts, exemplifies the integration of cutting-edge retinal photography technology with personalized patient care. The practice’s commitment to comprehensive ocular health assessment combines state-of-the-art diagnostic capabilities with the clinical expertise of Drs. Mark and Miranda Cannon.
Clinical Distinctions and Service Excellence:
- Implementation of advanced retinal imaging protocols utilizing current-generation technology platforms
- Comprehensive examination methodologies emphasizing thoroughness and diagnostic precision
- Exceptional patient satisfaction metrics evidenced by 240+ five-star reviews and a perfect 5.0-star rating
- Dual-location accessibility serving diverse Seattle metropolitan demographics
- Specialized expertise in early disease detection and preventive eye care strategies
Seattle Practice Locations:
- University Village Medical Center: 2602 NE University Village Street, Suite B | (206) 522-9323
- Pike Place Market Professional Center: 1906 Pike Place, Suite 8-B | (206) 448-7739
Commitment to Clinical Excellence
The practice’s approach to retinal photography exemplifies evidence-based medicine principles, utilizing advanced imaging modalities to enhance diagnostic accuracy while maintaining patient comfort and convenience. Whether addressing routine screening requirements or managing complex ocular pathology, Cannon EyeCare’s comprehensive retinal photography services provide the foundation for optimal long-term visual health outcomes.
To schedule your retinal photography consultation, contact either location directly to discuss your individual screening needs and establish a personalized ocular health monitoring protocol appropriate for your specific clinical circumstances.
References and Supporting Literature
Primary Research Sources
- Mass Eye and Ear Genomic Study (2024) – Landmark genomic analysis of 44,823 participants demonstrating correlations between retinal architecture and systemic disease risk across multiple organ systems.
Clinical Guidelines and Medical Standards
- Cleveland Clinic Retinal Imaging Protocols – Comprehensive clinical resource detailing retinal imaging procedures, safety protocols, and clinical applications from a leading academic medical center.
Technological Innovation Research
- National Eye Institute AI Enhancement Research (2025) – Breakthrough research demonstrating artificial intelligence applications achieving 100-fold improvements in retinal imaging speed with enhanced diagnostic quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the clinical capabilities and applications of retinal photography empowers patients to make informed decisions regarding their ocular health management. This comprehensive diagnostic modality offers unparalleled opportunities for early disease detection, longitudinal monitoring, and personalized risk assessment that can significantly impact long-term visual and systemic health outcomes.
As retinal photography technology continues to evolve through artificial intelligence integration and advanced imaging capabilities, its role in preventive medicine and comprehensive healthcare delivery will undoubtedly expand. Patients considering retinal photography should discuss the technology’s applications and benefits with their eye care providers to develop appropriate screening protocols tailored to their risk profiles and clinical circumstances.
Clinical Disclaimer: This publication provides educational information based on current medical literature and established clinical practices. Individual patients should consult qualified eye care professionals for personalized medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations specific to their clinical circumstances and health status.
FAQs
-
Retinal photography captures detailed images of your retina’s blood vessels, optic nerve, and macula using a special camera. It reveals eye conditions like diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, and glaucoma.